* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12 volt power supply
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
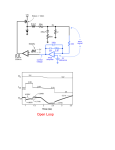
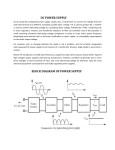
[Type text] FATIMA JINNAH RAWALPINDI WOMEN UNIVERSITY ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS PROJECT 12 Volt POWER SUPPLY SUBMITTED TO: SIR AHSAN ILYAS SUBMITTED BY: ZAINAB EJAZ........................BSE-2014-027 BSE-II GROUP-A DATE OF SUBMISSION: 19/05/2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRO 02 APPLICATION 02 COMPONENTS 03 TOOLS 04 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM 05 CONSTRUCTION 05 TEST 09 FINISH 10 WORKING 11 REFERENCES 14 1 12 VOLT POWER SUPPLY: INTRODUCTION: A power supply is an electronic device that supplies electric energy to an electrical load. The primary function of a power supply is to convert one form of electrical energy to another and, as a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are discrete, stand-alone devices, whereas others are built into larger devices along with their loads. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Every power supply must obtain the energy it supplies to its load, as well as any energy it consumes while performing that task, from an energy source. Depending on its design, a power supply may obtain energy from various types of energy sources, including electrical energy transmission systems, energy storage devices such as a batteries and fuel cells, electromechanical systems such as generators and alternators, solar power converters, or another power supply. All power supplies have a power input, which receives energy from the energy source, and a power output that delivers energy to the load. In most power supplies the power input and output consist of electrical connectors or hardwired circuit connections. APPLICATION: Power supplies are needed for most every bit of electronics equipment with the exception of battery-powered devices. Regulated power supply is the main component of electrical,electronics and as well as automation equipment. Mobile phone charger, oscilator, amplifier are needed the regulated power supply. Power supplies have wide uses in slectronic circuits.They are also used in computers. Making a Power Supply: Below is the guideline to make a 12 volt power supply. 2 COMPONENTS: Following components are required: Piece of veroboard Four 1N4001 diodes LM7812 regulator Transformer that has an output of 14v - 35v AC with an output current between 100mA to 1A, depending how much power you will need. (I found a 16v 200mA transformer in a broken alarm clock.) 1000uF - 4700uF capacitor 1uF capacitor Two 100nF capacitors Jumper wires (I used some plain wire as jumper wires) Resistor LED light 3 TOOLS: Following tools are required to make this power supply circuit: Soldering iron Solder, rosin core Wire cutters Solder sucker Wire strippers Digital multimeter A thing you can cut veroboard tracks. screwdriver Hot glue (To hold components down and make the power supply physically strong and sturdy.) And some other tools that you might find helpful. 4 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: CONSTRUCTION: Now, make the circuit on veroboard according to circuit diagram step by step. 5 6 Make sure you get good solder joints and no solder bridges, otherwise your power supply won't work! 7 TEST: After you had built your power supply, test it with your multimeter to make sure they are no solder bridges. FINISH: After you tested it, put it in a plastic box or something to protect you from shocks. But do not operate the power supply when it is not covered, it is very dangerous because of the mains voltage on the transformer, you will get badly shocked! 8 9 WORKING: A power supply is used to reduce the mains electricity at 240 volts AC down to some thing more useable, say 12 volts DC. Step Down Transformer A step down transformer will step down the voltage from the ac mains to the required voltage level. The output of the transformer is given as an input to the rectifier circuit. Rectification Rectifier is an electronic circuit consisting of diodes which carries out the rectification process. Rectification is the process of converting an alternating voltage or current into corresponding direct (dc) quantity. The input to a rectifier is ac whereas its output is unidirectional pulsating dc. Usually a full wave rectifier or a bridge rectifier is used to rectify both the half cycles of the ac supply (full wave rectification). Figure below shows a full wave bridge rectifier. 10 A bridge rectifier consists of four p-n junction diodes connected in the above shown manner. In the positive half cycle of the supply the voltage induced across the secondary of the electrical transformer i.e. VMN is positive. Therefore point E is positive with respect to F. Hence, diodes D3 and D2 are reversed biased and diodes D1 and D4 are forward biased. The diode D3 and D2 will act as open switches (practically there is some voltage drop) and diodes D1 andD4 will act as closed switches and will start conducting. Hence a rectified waveform appears at the output of the rectifier as shown in the first figure. When voltage induced in secondary i.e. VMN is negative than D3 and D2 are forward biased with the other two reversed biased and a positive voltage appears at the input of the filter. DC Filteration The rectified voltage from the rectifier is a pulsating dc voltage having very high ripple content. But this is not we want, we want a pure ripple free dc waveform. Hence a filter is used. Different types of filters are used such as capacitor filter, LC filter, Choke input filter, π type filter. Figure below shows a capacitor filter connected along the output of the rectifier and the resultant output waveform. As the instantaneous voltage starts increasing the capacitor charges, it charges till the waveform reaches its peak value. When the instantaneous value starts reducing the capacitor starts discharging exponentially and slowly through the load (input of the regulator in this case). Hence, an almost constant dc value having very less ripple content is obtained. Regulation This is the last block in a regulated DC power supply. The output voltage or current will change or fluctuate when there is change in the input from ac mains or due to change in load current at the output of the regulated power supply or due to other factors like temperature changes. This problem can be eliminated by using a regulator. A regulator will maintain the 11 output constant even when changes at the input or any other changes occur. Transistor series regulator, Fixed and variable IC regulators or a zener diode operated in the zener region can be used depending on their applications. IC’s like 78XX and 79XX are used to obtained fixed values of voltages at the output. With IC’s like LM 317 and 723 etc we can adjust the output voltage to a required constant value. Figure below shows the LM317 voltage regulator. The output voltage can be adjusted with adjusting the values of resistances R1 and R2. Usually coupling capacitors of values about 0.01µF to 10µF needs to be connected at the output and input to address input noise and output transients. Ideally the output voltage is given by Figure below shows the complete circuit of a regulated +5V DC power supply using transformer, bridge rectifier, filter (smoothing) and a fixed +5 V voltage regulator. Here we can use IC 7803(for 3V),7809(for 9 V),7812(for 12V) etc. …………..………………….…THE END……………………………………… 12 REFERENCES; http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_supply http://www.instructables.com/id/Make-a-simple-12-volt-powersupply/?ALLSTEPS http://www.instructables.com/id/How-to-solder/ http://www.instructables.com/id/Choosing-The-Resistor-To-Use-With-LEDs/ http://www.instructables.com/id/HOW-TO-READ-CIRCUIT-DIAGRAMS/ http://www.electrical4u.com/regulated-power-supply/ http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/Everything-You-Need-to-KnowAbout-Power-Supplies/181/2 https://www.kitronik.co.uk/blog/how-a-power-supply-works/ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/power-supply1.htm http://vr-zone.com/articles/how-power-supplies-work/11366.html http://www.britishtelephones.com/howpowr.htm 13