* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How to Break the Chain of Infection in your Outpatient Clinic/Medical
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
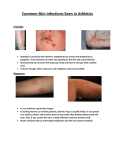
How to Break the Chain of Infection in your Outpatient Clinic/Medical Office INFECTIOUS AGENT (Germ that causes the disease) = MRSA (Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus) How to break the chain: SUSCEPTIBLE PERSON (How likely a person is to get sick after being exposed to the germ) = Anyone can get MRSA, but it is more likely if there are: Crowded living conditions Lack of cleanliness Frequent skin-to-skin contact Abraded skin Shared sports equipment Shared personal hygiene items Lack of healthcare access Overuse of antibiotics Kill or remove agent Identify individuals who are infected or colonized & treat appropriately Clean surfaces, then disinfect them with an EPA-registered disinfectant following manufacturer’s instructions Wash hands! RESERVOIR (Where the germ normally lives) = Skin and Nose of individuals infected or colonized with MRSA How to break the chain: Eliminate or reduce reservoir How to break the chain: Incise and drain (I & D) abscesses Do culture and sensitivity (C & S) of skin/soft tissue infection Wash hands! Prescribe antibiotics, if indicated, based on results of C & S report Consider decolonization Stop germs from entering Practice good personal hygiene Wash hands! Maintain a strong immune system through healthy living practices Take antibiotics appropriately – only when needed; take all prescribed MEANS OF TRANSMISSION (How the germ travels from the reservoir to a person) = Hands, Infection Site and Fomites (Fomites-items or environmental surfaces contaminated with body fluids containing MRSA) How to break the chain: Do not allow germs to escape and travel Wash hands / Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers Keep nails short. Acrylic nails should not be worn Avoid touching own nose, face while providing care Keep skin infections covered with clean, dry bandages Use contact precautions Clean and disinfect exam room and equipment Do not share sports equipment, towels, soap, clothing, razors, linens…. reviewed May 2011