* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
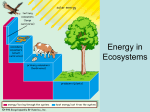
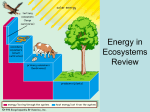
Download energy flows in ONE direction in an ecosystem!!!
Survey
Document related concepts
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
ECOLOGY- Chapters 2, 3, 4 & 5 What is ecology? What is a BIOTIC FACTOR? Examples __________________________________________________________________ What is an ABIOTIC FACTOR? Examples __________________________________________________________________ What is a HABITAT? What is a NICHE? LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION – HIERARCHY OF LIFE Organism (simplest): _________________________________________________________________ SPECIES _____________________________________________________________________ Population: _________________________________________________________________________ Community: ________________________________________________________________________ Ecosystem: _________________________________________________________________________ Biome: _____________________________________________________________________________ Biosphere (broadest): _________________________________________________________________ COMMUNITY INTERACTIONS: competition, predation, and symbioses COMPETITION: results from ______________________________________________________ organisms compete for _____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ may occur: where one species is eliminated PREDATION: results when one individual kills another organism___________________________ individual that is killed called __________________________ this is one way that ______________________________________________ occurs Anti-Predator Defenses Camouflage - ________________________________________________________________________ Mimicry - __________________________________________________________________________ Warning Coloration - ________________________________________________________________ Protective Coverings - ________________________________________________________________ Secondary Compounds - ______________________________________________________________ SYMBIOTIC RELATIONSHIPS (SYMBIOSES): mutualism, commensalism, parasitism MUTUALISM: ___________________________________________________________________________ examples ___________________________________________________________________________ COMMENSALISM:_______________________________________________________________________ examples ___________________________________________________________________________ PARASITISM:___________________________________________________________________________ examples ___________________________________________________________________________ HOW LIVING THINGS MEET THEIR ENERGY NEEDS… What is the energy source for most living things? _________________ Autotrophs or _______________________ or “self-feeders” can produce _______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Autotrophs can be photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs…. Photoautotrophs inclue ____________________________________________ and perform… photosynthesis which uses _____________ energy to produce carbohydrates/food/fuel Chemoautotrophs include __________________________________________ and perform… chemosynthesis which uses ____________ energy to produce carbohydrates/food/fuel Plant Responses (Tropisms): Phototropism = response toward _____________________ Geo/Gravitropism = response toward ___________________ Thigmotropism = response to _________________________________ Heterotrophs or __________________ or “other feeders” cannot produce their food and ________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ There are many different kinds of heterotrophs including…. Herbivores = feed on _____________________________ Carnivores = feed on _____________________________ Omnivores = feed on _____________________________ Detritivores = feed on detritus (dead organic matter) – include _________________________________ Decomposers = break down organic matter and recycle nutrients – include _______________________ ENERGY FLOW THROUGH AN ECOSYSTEM THE SUN energy flows in ONE direction in an ecosystem!!! from ________________________________________________ What is a food chain? What is a food web? TROPHIC LEVELS (FEEDING LEVELS): each step in a food chain or food web is called a _______________________________ a trophic level indicates an organism’s position in the sequence of ___________________________ most ecosystems have only ________________ trophic levels TROPHIC LEVELS (FEEDING LEVELS) : producers – primary (1st order) consumers secondary (2nd order) consumers tertiary (3rd order) consumers quaternary (4th order) consumers trophic levels can be represented with an ______________________________________________ which shows the relative amounts of ________________________________________________ contained within each level ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS: energy pyramid, biomass pyramid, pyramid of numbers ENERGY PYRAMID: shows the relative amount of ____________________ available at each trophic level. only about ________ of the energy available at each level is transferred to the next about ________ of the energy at each level is lost as heat or used in life processes BIOMASS PYRAMID: represents the amount of biomass ( ____________________________) at each trophic level represents the amount of potential _________________ available for each trophic level typically, the greatest biomass is at the __________________________ of the pyramid PYRAMID OF NUMBERS: represents the relative _________________________________________ at each trophic level BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES elements, chemical compounds and other forms of matter MUST BE RECYCLED and are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another through biogeochemical cycles WATER CYCLE (also called the __________________________ cycle) is the _________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Evaporation _________________________________________________________________________ Transpiration _________________________________________________________________ Perspiration ___________________________________________________________________ Condensation ________________________________________________________________________ Precipitation _________________________________________________________________________ Why is water important? __________________________________________________________________ CARBON AND OXYGEN CYCLE ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Decomposition ______________________________________________________________________ Combustion _________________________________________________________________________ Respiration __________________________________________________________________________ Why are C and O important? _______________________________________________________________ NITROGEN CYCLE _______________________________________________________________________ Nitrogen Fixation = ___________________________________________________________________ Denitrication = ______________________________________________________________________ Why is N important? _____________________________________________________________________ PHOSPHORUS CYCLE ____________________________________________________________________ How is the P cycle different? _______________________________________________________________ Why is P important? ______________________________________________________________________ COMMUNITIES Limiting Factor – biotic or abiotic factors that restricts the numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms. Examples _________________________________________________________________ ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION – ____________________________________________________________ occurs when a NEW LAND AREA is exposed or when an EXISTING LAND AREA is disturbed succession usually culminates in a climax community (a stable, final community) Climax Community…. the end result of succession, the final (stable) community to inhabit an area PRIMARY SUCCESSION – _____________________________________________________________ Examples… volcanic islands, bare rock, glacier melting Pioneer Species – _______________________________________________________________ Examples ….mosses, lichens, other nonvascular plants Lichen = __________________________________________________________ SECONDARY SUCCESSION – _________________________________________________________ LATITUDE AFFECTS CLIMATE • • latitude = the distance (N or S) of any point on Earth from the equator. climate is directly ____________________________________________________________________ CLIMATE … the average year to year conditions of … WEATHER … the day to day conditions of … GREENHOUSE EFFECT - a natural phenomenon that occurs when heat is retained (trapped) by the atmosphere – the greenhouse effect helps to keep the planet warm and life on Earth possible ________________________________________________ and other gases in the atmosphere trap heat the atmosphere acts like an insulating _________________________________________________ some scientists believe that An enhanced greenhouse effect = ______________________________ IN SUMMARY… Latitude __________________________________ Climate ________________________________ Weather _____________________________ Precipitation __________________________ (vegetation) Flora ___________________________ (animal life) BIOME – a large geographical area having… • • characteristic temperature range and _____________________________________________________ characteristic ________________________________________________________________________ TUNDRA • • • • • • cold & treeless; covers 1/5 of world’s land little precipitation (mostly frozen) flora - ______________________________________________________________________________ fauna - _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________: permanently frozen layer of soil under surface summer can cause boggy ponds & different fauna TAIGA or BOREAL FOREST or CONIFEROUS FOREST • • • south of the tundra; in the N hemisphere flora: ______________________________________________________________________________ fauna: _____________________________________________________________________________ TEMPERATE DECIDUOUS FOREST (YOU live here!) • • • • trees that lose their leaves are found here = _______________________________ trees warmer winter and longer summers = ___________________________ flora: _____________________________________________________________________________ fauna: ____________________________________________________________________________ TEMPERATE GRASSLAND • • • • • • also known as prairies (“the bread basket”) dominated by ____________________________________ less rainfall; not many tall trees ____________________________________ soil flora: ______________________________________________________________________________ fauna: _____________________________________________________________________________ TROPICAL GRASSLAND or TROPICAL SAVANNA • • • can be in tropical or subtropical regions flora: _______________________________________________________________________________ fauna: ______________________________________________________________________________ DESERT – there are hot deserts and cold deserts • • • • • less than _____________________ (25 cm) rainfall per year can be cold because of the low humidity (moisture) sparse vegetation that have adaptations for the dry conditions __________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ flora: _______________________________________________________________________________ fauna: ______________________________________________________________________________ TROPICAL RAINFOREST • most productive biome – GREATEST BIODIVERSITY BIODIVERSITY = ______________________________________________________________________ 3 KINDS OF BIODIVERSITY – SPECIES DIVERSITY, ECOSYSTEM DIVERSITY, GENETIC DIVERSITY • • • • • • most of the world’s species live here warm year round; little variation in temperature canopy formed from a continuous layer of treetops that shades the forest floor precipitation ____________ inches per year; rains almost daily flora: _______________________________________________________________________________ fauna: ______________________________________________________________________________ AQUATIC/WATER ECOSYSTEMS are determined by water chemistry (pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen) depth, flow, and temperature SALTWATER _______________________________________________________________________ Marine areas include ____________________________________________________________ these areas make up ______% of water on Earth FRESHWATER ______________________________________________________________________ make up only ______% of water on Earth Most freshwater ________________________________________________________________ GROUNDWATER _____________________________________________________________ *There are transitional aquatic ecosystems where saltwater and freshwater merge wetlands and estuaries ESTUARY - wetlands formed where rivers (fresh water) meet salt water • these areas are affected by the rise and fall of tides; are usually shallow • serve as spawning and nursery grounds for many aquatic species POPULATION DENSITY – ________________________________________________________________ Factors that may affect population density….. DENSITY INDEPENDENT FACTOR – affects a population regardless of the _____________________ of the population - usually abiotic; weather events Examples: ____________________________________________________________________ DENSITY DEPENDENT FACTOR – affects a population on the basis of the ___________________________ of organisms Examples: ____________________________________________________________________ • • Immigration – movement of individuals ______________ an area. Emigration – movement of individuals ________________ an area. CARRYING CAPACITY - ________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH IS CAUSING… • • • • severe overcrowding in some areas ___________________________ in energy demands a need for an increased food supply and increased waste disposal very rapid ecological change (habitat destruction,….) * The world’s population tripled from 1930-2000 and is expected to double again from 2000-2050