* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy and Physiology of Vegetable Plants
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
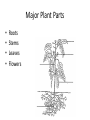
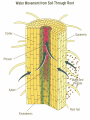
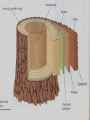
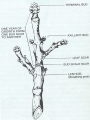
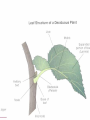
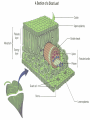
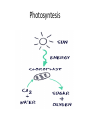
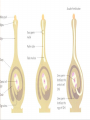
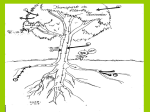
Anatomy and Physiology of Vegetable Plants Divisions of Plant Physiology Major Plant Parts • • • • Roots Stems Leaves Flowers Roots Functions: • Absorb water and nutrients • Anchor the plant, and support the above ground part of the plant. • Store food. Roots Root Systems: • Fibrous: A system that has no dominant primary root. • Tap: A system composed of one primary root and many secondary roots that branch off. Fibrous Tap Roots Roots • Primary Root: The first root to emerge at germination. May become the main tap root. • Secondary Roots: Roots that branch out from the primary root. • Apical Meristem: Area at the tip of the root where new cells develop Roots • Healthy Roots: Roots are white or nearly white, and smell fresh. • Unhealthy Roots: Roots are black, brown, or dark orange and smell rotten and sour. Stems Functions: • Support the leaves, and position them so they can receive as much sunlight as possible • Responsible for the size and shape of the plant. • Move water, minerals, and manufactured food throughout the whole plant. • Green stems produce food through photosynthesis. Stem Internal Structure Xylem: (Xylem Up) • Tissue responsible for carrying water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves. It is located near the center of the stem. Phloem: (Phloem Down) • Tissue responsible for carrying food produced in the leaf to the rest of the plant. The phloem is usually located near the outside of the stem. Cambium: • Tissue responsible for the production of new xylum and phloem. It is found between the xylum and phloem. Stems • Specialized Stems • Bulbs: Short flattened stem which has several fleshy leaves. Bulbs are found beneath the soil. Example: Onions • Corm: Sphyrical structure similar to a bulb. Example: Gladiolus Stems • Specialized Stems • Rhizome: Thick underground stem which lies horizontally. • Example: Mother in Law’s Tongue • Stolon: Horizontal stem which lies above the ground (often called runners). • Example: Strawberry runners Stems Specialized Stems • Tuber: Rhizome with a tip that is swollen with stored food. Example: Potatoes. Leaves Function: • Produce food for the plant. They are designed to efficiently collect light and CO2 and use them to make energy. Leaves Leaf Parts • Leaf Blade: Large, broad, flat surface whose job is to collect sunlight • Petiole: supports the leaf and holds it away from the stem. • Midrib: Main vein running down the center of the leaf. It helps hold the leaf so it is facing the sun. Leaves Leaf Types • Simple leaf: Has only one leaf on the petiole. • Compound leaf: A leaf with multiple blades. Leaves Vein Patterns • Parallel: Veins never cross. Found in monocots. • Netted: Veins form a network. Found in Dicots. Leaves Leaf Layers: • Cuticle: The top waxy, non-cellular part of the leaf. Its job is to prevent water escaping. • Epidermis: Skin like layer of cells found on both the top and bottom of the leaf. Its job is to protect the leaf. Leaves • Leaf Layers – Palisade Mesophyll: A layer of cells standing on end directly below the upper epidermis. This area is responsible for photosynthesis. – Spongy Mesophyll: Loosely packed cells located beneath the palasade mesophyll. This area is responsible for holding the products of photosynthesis. Leaves • Leaf Layers – Stomata: Holes in the lower epidermis responsible for gas exchange. – Guard Cells: Surround the stomata’s and open and close them. Leaf Layers Photosynthesis “A chemical process by which a plant turns light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugar.” • The plant uses water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a sugar) with the by-product of oxygen. • These chemical reactions take place inside the cells near the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are filled with Chlorphyll which makes the plants green and are responsible for the process of photosynthesis Photosyntesis Respiration Cellular Respiration: The opposite of photosynthesis. This process breaks sugars down so plants can use them. • Similar to digestion in animals. • Takes place in a place in the cell called the mitochondria. Flowers Flower Parts -- Male • Stamen: Male part of the flower. Filament: Stalk like in the stamen that holds up the anther Anther: Sack-like structure that contains pollen. Pollen grains are released from the anther that contains sperm. Staminate: Flowers that have only male parts. Flowers Flower Parts – Female • Pistil: Female part of the flower Stigma: Sticky part of the pistil that is receptive to pollen. Style: Rod shaped middle part that has a swollen base (ovary) containing eggs Flowers Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Two parents (meiosis) • The stamen releases pollen. • Pollen is carried by wind, gravity, animals, or insects to the stigma of another flower. (This is when pollination occurs) • The pollen moves from the stigma down through in a pollen tube the style depositing sperm in the ovary. Flowers Sexual Reproduction in Plants • The sperm gets deposited in the ovary, fertilization occurs. • After fertilization the ovary and surrounding tissue start to enlarge to become a fruit and the fertilized eggs become seeds. Flowers Flower Types: • Perfect Flower: Has both male and female parts. • Imperfect Flower: A flower that is missing either male or female parts. • Complete Flower: Flowers that have sepals, petals, pistils, and stamens. • Incomplete Flowers: A flower that is missing sepals, petals, pistils, or stamen. Note: Imperfect Flowers are always incomplete. Incomplete flowers may or may not be imperfect Light • Plants need the colors blue and red to activate chlorophyll. • Light bulbs are deficient in the color blue. • Fluorescent tubes are deficient in the color red. • Special grow lights are made that carry the correct blue and red wavelengths. Light • Light intensity is measured in foot candles, the amount of light given off by a candle a foot away. • Plants have adapted to survive in either high, partial, or low light intensities. Light • Photoperiod: The length of daylight. • Short Day Plants: Plants that begin to flower when the nights are over 12 hours long. • Long Day Plants: Begin to flower when the nights are under 12 hours long. • Neutral Plants: Flowering response is unaffected by day length. Temperature • Hardiness: A plants ability to withstand cold temperatures. • The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is a good reference to locate your hardiness zone. • Wilting: A condition caused by excess heat and dryness. When a plant wilts it closes its’ stomata and the cells lose their turgor pressure. Air • Oxygen is needed by the plant for respiration. It is obtained by the roots and is needed by the plant for respiration. • Carbon Dioxide is needed by the plant for photosynthesis. It is obtained through the stomata Water • Plants get most of the water through their roots. Some small quantities are also obtained through the stems. • Plants should be watered all the way through the root zone to encourage even root growth. • Container grown plants; containers should have drainage holes so the water can drain and allow oxygen into the root zone. Plant Hormones Regulate Growth • Auxins: Growth hormones produced by the apical meristem. They encourage height growth, and discourage lateral growth • Cytokinins: Produced in roots and seeds, and are responsible for cell division and differentiation. • Ethylene: Produced by ripening fruit, it stimulates flowering, and ripening. • Gibberellins: Produced in stems, roots, and young leaves. They are responsible for internodal elongation. • Abscisic Acid: Found in seeds. A hormone which inhibits growth. Giberrellins Effect on dwarf bean plants Ethylene The effect of Auxins Plant Hormones Regulate Growth Commercial Uses: • A-rest, B-Nine, Cycocel, Florel: Used on poinsettias, Easter Lilies, and Chrysanthemums to reduce size to make a shorter bushier, and more attractive plant. • Rootone and Hormodin: Used to help plants root more quickly. • Ethylene gas: Used to ripen bananas when they get to market. Used to induce flowering in pineapple crops. Common Diseases that Affect Plant Parts Roots • Roots discolored, mushy. Check soil moisture and watering • Root rot caused by one of several common fungi Common Diseases that Affect Plant Parts Stems • Black or dark cankers on stem. (Submit samples to a diagnostic clinic for confirmation) – Early blight (Alternaria), tomato spotted wilt virus/impatiens necrotic spot virus, bacterial canker Common Diseases that Affect Plant Parts Leaves • Black or dark brown spots. Lesions have margins or concentric rings. Lower leaves commonly affected – Early blight (Alternaria) • Spots on leaves with white or gray centers surrounded by dark black or brown margins – Septoria leaf spot Common Diseases that Affect Plant Parts Leaves (continued) • Lower leaves turn down, leaf edges brown – Bacterial canker • Leaf spotting, concentric rings and necrotic (dead) leaf margins may or may not be present, leaf tissue stiff, not flaccid – Tomato spotted wilt virus/impatiens necrotic spot virus Common Diseases that Affect Plant Parts Fruit • Blossom end flattened and black – Blossom end rot • Pin pricks surrounded by yellow – Stink bugs • Ring spots on fruit – Tomato spotted wilt virus/impatiens necrotic spot virus Remedies NOTE: STRICTLY FOLLOW ALL LABEL INSTRUCTIONS AND BE SURE THE PRODUCT IS SAFE FOR YOUR APPLICATION. • Fungal – Terraclor, Ridomil or other fungicide • Blight – Destroy affected plants, use Chlorothalonil or Mancozeb for control in neighbors • Powdery Mildew – 2 tsp baking soda/gallon water; Benomyl and chlorothalonil for vine crops, and sulfur on beans and peas • Mosaic Virus – No remedy – destroy plants • Bacterial – Copper fungicide can help with bacterial leaf spots • Insects – Thrips, Aphids, others are vectors for diseases; use Malathion or Diazinon for control • Contact the LSU AgCenter Sources and Acknowledgements • Univ. of Georgia and the Atlanta Master Gardeners Assn. • Wikipedia • LSU AgCenter • Numerous “on-line” publications from LSU, Univ. of Alabama, Miss. State Univ., Univ. of N. Carolina, Univ. of Michigan • Plant Physiology.org • Numerous research foundation publications • Free online medical and botanical dictionaries