* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download One and Two digit Addition and Subtraction - Perfect Math
Survey
Document related concepts
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical calculator wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
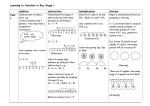
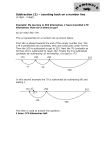
One and Two digit Addition and Subtraction Peter Gibby Counting • We are all familiar with the number line, we start at 1 then go to 2 then 3, 4, 5 and so on. • Addition is just counting up so many times. • We use the plus sign (+) to represent addition. • So if we add one and one, 1+1, we get 2. • We use the equals sign (=) to represent the new value. • Every number has a number before and after it so any two numbers can be added together, even larger numbers. • 5+3=8 • To get that we counted 3 values higher than 5 – 5, 6 (1), 7 (2), 8 (3) • Notice that we don’t count the number 5, just the 3 numbers following it. Subtraction • Subtraction is just backwards addition or counting. • We start at a larger number and take a value out of it. We use the subtraction sign (-) to represent this. • We know that 3+2=5, so 5-2=3 because – 5, 4 (1), 3 (2) • Notice that we still don’t count the number we start on Two Digit Numbers • Counting to 9 is great, but there are a lot more numbers than that. We use our ten digits to represent all these numbers. • When we see a two digit number we know that the first value is the tens place. This means instead of representing a value of one, it takes a value of ten. • What we do is we count by tens when we use the first digit, so – 14 is the same thing as ten plus four (10+4=14) – 26 is the same as, 10 (1), 20 (2), twenty plus 6 (20+6=26) Adding Two Digit Numbers Together • When we add two digit numbers together, we count based on whether it was in the ten’s place or the one’s place, so – 23+14= • 2+1=3 • 3+4=7 • 37 (always put the ten’s place first) Subtracting Two Digit Numbers • Subtracting is still just the opposite of adding. Instead of going up, we go down. We know that 12+15=27 so, – 27-15=12 – If you can’t see how we got that you can just count backwards for each digit, – 27-15 • 2-1=1 • 7-5=2 • 12 (We still keep the ten’s place first)