* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 - Nervous and Immune Systems Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
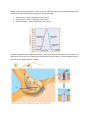
Nervous System Important Vocabulary Sensory Input Myelin Sheath Synapse Integration Synapse Sensation of Touch Motor Output Membrane Potential Sensation of Hearing Signal Transduction Pathway Na+/K+ Pump Sensation of Taste Neuron Depolarization Sensation of Smell Cell Body Repolarization Sensation of Sight Dendrite Hyperpolarization Axon Saltatory Conduction How has the nervous system evolved over time? In what ways do more recent organisms have more evolved nervous systems? Elaborate on the three major steps involved in receiving and responding to a stimulus. Sensory input Integration Motor Output Be able to identify and describe the major structures of the neuron. Cell Body Dendrite Axon Myelin Sheath Synaptic Terminal Be able to describe the graph below. There are several important steps that are described in the graph and you will need to know what is taking place during each stage. Depolarization – what is happening in the neuron? Repolarization – what is happening in the neuron? Hyperpolarization – what is happening in the neuron? Synapses are gaps between neighboring neurons. The process by which an action potential moves from one neuron to the next is very important to the transport of nerve impulses. Use the diagram below to describe what is happening at the synapse. Sensory reception, while different based on the specific sense, is very similar in how it works. Below are the 5 major senses. Be able to describe and understand how each sense works. (Focus on what is different between the senses.) Identify the major sensory receptors: Mechanoreceptors, nociceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, electromagnetic receptors Touch: how does the sense of touch work with receiving stimuli from the outside environment? o What kind of receptors are found in the skin? Hearing: how does a stimulus move from the outside world (as sound waves) to the brain (as an electrical signal) o What are the major structures involved in this process? Taste and Smell: how does a stimulus (chemical) move through the nose and mouth to the brain (as an electrical signal)? o What are some major structures involved in this process? Sight: understand how a visual stimulus (light energy) moves to the brain (as an electrical signal). o Be aware of the evolution of sight in animals. How has it changed over time? o What are rods? What are cones? How do they play a role in sight? Immune System Important Vocabulary Innate Immunity MHC Class I Memory Cells Phagocytes MHC Class II B Lymphocytes Macrophage Antigen T Lymphocytes Monocyte Primary Immune Response Humoral Immunity Histamine Secondary Immune Response Cell-Mediated What is meant by innate immunity? List several basic defenses that are considered innate. Phagocytes are also considered an innate defense. o What are macrophages? o What are monocytes o How do these WBCs play a role in the immune system? An inflammatory response occurs when the body is attacked by a foreign material. What is the overall process by which your body initiates an inflammatory response? (We looked at several major steps in class that include releasing histamine and calling in phagocytes) What chemical signal molecule is used to initiate an inflammatory response? Immune responses are triggered by the presence of surface proteins that promote the creation of antibodies. What are these surface proteins called? What protein structures are used to identify these surface proteins? Using what you know about the production and transport of proteins, how would a cell get these proteins to the cell membrane? How are specific immune response different from innate immunities? What is a primary immune response? What is a secondary immune response? How are these two immune responses different? Specific Immune Responses involve several important WBCs (Lymphocytes) in animals. How do B Lymphocytes play a role in specific immune responses? How do T Lymphocytes play a role in specific immune responses? o Describe Helper T Cells o Describe Cytotoxic T Cells Describe Humoral Immunity Be able to trace the process from initial infection by a pathogen to production of antibodies Describe Cell-Mediated Immunity Be able to trace the process from initial infection by a pathogen to destruction of infected cells by cytotoxic T Cells Interleukin 2 Interleukin 2 Antibodies are produced through the humoral immune response o How do antibodies help fight pathogens in the body? What are allergies? ****For the information below, you may need to use outside resources to find this material**** What are autoimmune disorders? How are these caused? List several common autoimmune disorders. What are immunodeficiency disorders? How are these caused? List several common immunodeficiency disorders.