* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 21 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
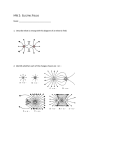
Chapter 21 Notes Electric Fields Electric fields – these relate the force (N) exerted on a charge (C) to its size In other words, the larger the charge… If the size of the charge is doubled, so is the force. Formula: Electric Field = ____F_____ q’ F = force in Newtons q’ = test charge in Coulombs (C) Electric Field units are N/C (Newton/Coulombs) *the direction of the electric field will be the direction of the force on the positive charge *Electric Field lines – see page 485 figure 21-2 The distance between the lines will indicate the strength of the field – the closer the lines the stronger the field Lines always leave the positive and enter the negative Example problems: 1. A negative charge of 2.0 X 10-8C experiences a force of 0.06N to the right in an electric field. What are the field magnitude and direction? 2. A positive test charge of 5.0 x 10-4C is in an electric field that exerts a force of 2.5 x 10-4 N. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the location of the test charge?