* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.2b
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Frémont Emancipation wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
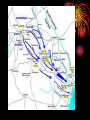
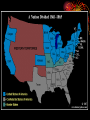
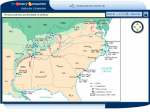
The Civil War And Reconstruction 3.2b • Summarize the course of the Civil War and its impact on democracy, including the major turning points; the impact of the Emancipation Proclamation; the unequal treatment afforded to AfricanAmerican military units; the geographic , political , and economic factors involved in the defeat of the Confederacy; and the ultimate defeat of the idea of secession. The Emancipation Proclamation • Lincoln demonstrated his political skill by his handling of the issue of emancipation of slaves. • Lincoln initially hesitated to free the slaves because he feared this would undermine the unity of the North. • ***When emancipation was announced it was promoted as a military measure against the South. • However, the Emancipation Proclamation was a political and diplomatic document. • ***Saw slavery as a “weapon of war” • By making a goal of the war the liberation of slaves, Lincoln made it impossible for the British, whose population was strongly opposed to slavery, to continue to support the Southern states. • ***By announcing his attention to issue the Proclamation in the fall and not making it effective until the 1st of the year he gave the South one last chance to make peace. The Emancipation Proclamation • ***The Emancipation Proclamation did not immediately free any slaves. • It did not attempt to free slaves in regions under Union control. • Only states in rebellion on January 1, 1863 were commanded to free their slaves and Confederates were not likely to obey the President of the United States. • Slaves were freed as their homeland was captured by Union forces or as they fled toward the Union Army. The first reading of the Emancipation Proclamation Gettysburg (July 1-4, 1863) • Lee had again invaded the North • General Meade followed his army and they met near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania • Lee was defeated so badly that he was never able to take the offensive again. • Lincoln issues his famous Gettysburg Address. The Battle of Vicksburg, May 15th to July 4th, 1863 • Vicksburg was the last Confederate strong point on the Mississippi and Lincoln knew it was one of the keys to winning the war. • After several aborted attacks Grant and his soldiers laid siege to the city. • The town finally surrendered on July 4th, 1863 because they were starving and had been reduced to eating horses, dogs and rats. • The victory gave the Union control over the Mississippi River. Sherman’s March • General Grant became head of Union armies and changed the Union strategy to ‘total war.” • Grant placed William T. Sherman in command of the western armies and orders him to march from Tennessee to Savannah, Georgia. • During this famous march to the sea Sherman and his men destroyed everything. Civilians homes and businesses were burned making this the first modern war. • He stopped in Atlanta, Georgia and when he left he burned the city. • He also stopped and burned much of Columbia, S.C. African-Americans and the war • As you know the Emancipation Proclamation made it possible for AfricanAmericans to serve in the U.S. army and navy. • Many did so gallantly. • However, they served in segregated units and served under white officers. • They were poorly supplied and paid less than their white counterparts. • The most famous Unit was the 54th Massachusetts Regiment made famous by the movie Glory. (courageous assault on Ft. Wagner near Charleston) • Over 100,000 blacks served in the Union Army. Col. Shaw Veterans Day March of the 54th The Election of 1864 • By 1864 many people were tired of the war and the killing. • The Democratic Party nominated former General George B. McClellan to run against Lincoln. • His platform included a negotiated peace with the south that would allow slavery to survive. • Before the election Sherman captured Atlanta and signaled that the Union victory was in reach assuring Lincoln’s re-election. Union Victory-Lincoln finds the right general • Grant takes command and begins a non-stop assault on Lee. Grant changes from the Anaconda Plan to the idea of “total war” • Grant is often called the butcher because he lost 65,000 men in just two months. • However, Grant could afford the loses because of overwhelming numbers. Lee could not and kept retreating. • Eventually Lee and his army were surround near Richmond, Virginia. • When Lee tried to escape he was caught in the open by Grant’s forces and decided to surrender. • The Surrender document was signed on April 9th, 1865 at Appomattox Courthouse. • The war was essentially over.