* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model • The shape of a
Survey
Document related concepts
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
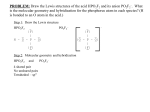
Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes • Summarize the VSEPR bonding theory. • Predict the shape of a molecule. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- VSEPR Model • The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. • Molecular geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model, or VSEPR model which minimizes the repulsion of shared and unshared atoms around the central atom. Section 8.4 VSEPR Model (cont.) • Electron pairs repel each other and cause molecules to be in fixed positions relative to each other. • Unshared electron pairs also determine the shape of a molecule. • Electron pairs are located in a molecule as far apart as they can be. Section 8.4 VSEPR Model (cont.) • Start with the central atom. • Identify how many bonds or shared pairs are on the central atom. • Then identify how many unshared pairs or lone pairs are on the central atom. • Each combination of shared and unshared pairs will represent a specific molecular shape. Section 8.4 Shapes of Molecules Section 8.4 Shapes of Molecules (cont.) Section 8.4 Shapes of Molecules (cont.) Shapes of Molecules (cont.) • Remember to focus on the central atom. Here is a review of the shapes: Linear- 1 bond, no central atom - 2 bonds, no unshared pairs of eBent- 2 bonds, 2 unshared pairs of ePyramidal- 3 bonds, 1 unshared pair of eTriangular planar or Trigonal3 bonds, no unshared pair of eTetrahedral- 4 bonds, no unshared pair of eTrigonal Bipyramidal5 bonds, no unshared pair of eOctahedral- 6 bonds, no unshared pairs of e- AB2 AB2E2 AB3E AB3 AB4 AB5 AB6 Shapes of Molecules (cont.) Predicting the Shape of Molecules Steps: 1. Draw the Lewis Structure for the compound. 2. Identify the central atom as A. 3. Identify the number of bonds (B) around the central atom. Use a subscript to label the number. 4. Identify the number of unshared pairs of electrons (E) on the central atom. Write out the abbreviations and figure out the shape.