* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dosage Growth Defect Overexpression of one gene in the presence
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
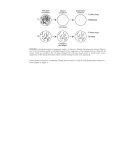
Dosage Growth Defect Dosage Lethality Dosage Rescue Phenotypic Enhancement Phenotypic Suppression Synthetic Growth Defect Synthetic Rescue Synthetic Lethality Negative Genetic Positive Genetic Overexpression of one gene in the presence of a mutant causes significant growth defect compared to mutant alone. Overexpression of one gene in the presence of a mutant is lethal while the mutated gene alone is not. Growth defect or lethality of a single mutant is rescue by the over-expression of a second gene. Double mutant shows marked increase in non-growth phenotypic effect in comparison to either single mutant. Double mutant shows marked decrease in non-growth phenotypic effect in comparison to either single mutant. Double mutant shows marked decrease in growth in comparison to either single mutant. Growth defect or lethality of a single mutant is rescued by the mutation in a second gene. Double mutant is lethal while either single mutant is non-lethal. Double mutant shows marked decrease in growth in comparison to either single mutant, as determined by high-throughput assays with growth scores. Double mutant shows marked increase in growth in comparison to either single mutant, as determined by high-throughput assays with growth scores. Table 1: Table S1. Definitions of types of genetic interaction. The types of genetic interactions described above are defined by BioGRID, http://thebiogrid.org. 1