* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Covariance and contravariance of vectors wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Tensors in curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
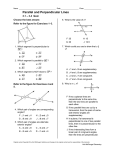
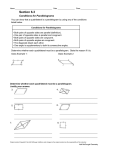
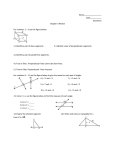
8-5 Coordinate Geometry Preview Warm Up California Standards Lesson Presentation Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Warm Up Complete each sentence. 1. Two lines in a plane that never meet are called parallel lines. 2. Perpendicular lines intersect at right angles. 3. The symbol || means that lines are parallel . 4. When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, all of the acute angles are congruent. Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry California Standards MG3.2 Understand and use coordinate graphs to plot simple figures, determine lengths and areas related to them, and determine their image under translations and reflections. Also covered: Holt CA Course 1 AF3.3 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Vocabulary polygon quadrilateral trapezoid parallelogram rectangle rhombus square Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry In computer graphics, a coordinate system is used to create images, from simple geometric figures to realistic figures used in movies. Properties of the coordinate plane can be used to find information about figures in the plane, such as whether lines in the plane are parallel. Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines • Any two nonvertical lines with equal slopes are parallel. Any two vertical lines are parallel. • Any two nonvertical lines whose slope have a product of –1 are perpendicular. Vertical and horizontal lines are perpendicular. Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Additional Example 1: Finding Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Which lines are parallel? Which lines are perpendicular? Step 1 Find the slope of each line. 3 2 3 slope of GH = 5 3 slope of PQ = 5 –2 2 slope of CD = or – 3 3 3 slope of QR = or –1 –3 slope of EF = Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Additional Example 1 Continued Which lines are parallel? Which lines are perpendicular? Step 2 Compare the slopes. GH || PQ The slopes are equal. 3 3 = 5 5 EF CD The slopes have a product 2 3 of –1: •– = –1 3 2 Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Check It Out! Example 1 Which lines are parallel? Which lines are perpendicular? Step 1 Find the slope of each line. –6 –3 or 4 2 –2 slope of CD = 3 –4 –2 slope of EF = or 6 3 2 slope of GH = 3 3 slope of JK = or 1 3 slope of AB = Holt CA Course 1 A C K D E H J B G F 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Check It Out! Example 1 Continued Which lines are parallel? Which lines are perpendicular? Step 2 Compare the slopes. CD || EF A –2 –2 The slopes are equal. = 3 3 C K GH AB The slopes have a product 3 2 of –1: •– = –1 2 3 Holt CA Course 1 D E H J B G F 8-5 Coordinate Geometry A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments called sides. Each side meets exactly two other sides, one on each end, in a common endpoint. Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides and four angles. Quadrilaterals with certain properties are given additional names. Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Additional Example 2: Using Coordinates to Classify Quadrilaterals Graph the quadrilateral with the given vertices. Give all the names that apply to the quadrilateral. A(3, –2), B(2, –1), C(4, 3), D(5, 2) CD || BA and BC || AD parallelogram Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Check It Out! Example 2 Graph the quadrilateral with the given vertices. Give all the names that apply to the quadrilateral. R(–3, 1), S(–4, 2), T(–3, 3), U(–2, 2) TU || SR and ST || RU TURU, RURS, RSST and STTU 2 pairs of parallel sides, 4 right angles. parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square Holt CA Course 1 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Additional Example 3: Finding the Coordinates of a Missing Vertex Find the coordinates of the missing vertex. Rectangle WXYZ with W(–2, 2), X(3, 2), and Y(3, –4) Step 1 Graph and connect the given points. W X Step 2 Complete the figure to find the missing vertex. The coordinates of Z are (–2, –4). Holt CA Course 1 Z Y 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Check It Out! Example 3 Find the coordinates of the missing vertex. Rectangle JKLM with J(– 1, 2), K(4, 2), and L(4, –1) Step 1 Graph and connect the given points. Step 2 Complete the figure to find the missing vertex. The coordinates of M are (–1, –1). Holt CA Course 1 J K M L 8-5 Coordinate Geometry Lesson Quiz Determine the slope of each line. 1. PQ 1 2. MN – 10 3 3. MQ 8 4. NP 7 5. Which pair of lines are parallel? MN, RQ Holt CA Course 1