* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
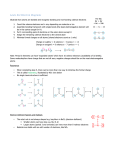
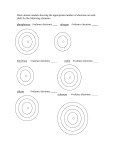
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum Numbers (n,l,ml,ms), when they are allowed, how they describe the electron state, and how they relate to: Energy levels, orbitals (number allowed, shapes, sizes), electrons and spin Pauli Exclusion Principle Electron configurations of a given atom 1s22s22p6…etc Short/abbreviated method, i.e. [noble gas]…the rest Orbital diagrams (and Hund’s Rule) Exceptions to predicted electron configs (Cu,Ag,Au) Valence electrons Periodic table and electron configs (e.g. alkaline earth metals last sublevel ns2 Periodic Trends: Ionization Energy, Atomic Radius, Electron Affinity, Electronegativity (Ch8) Chapter 8 – Chemical Bonding Covalent vs Ionic bond – energy model Ionic bond, coulomb’s law and lattice energy (they all relate) Ionic radius trends (atom vs ion, and compare isoelectronic series) Bond energies to calculate Hrxn (Ebonds broken – Ebonds formed) Lewis structures predict which atoms bond to which and nonbonding electrons (lone pair) 2 valence electrons max: H, He 8 valence electrons max: 2nd row elements <8 valence electrons exceptions: Be=4, B=6 (formal charge) >8 valence electrons: 3rd row elements and below Consider formal charges in evaluating structures When to draw resonance structures, and how many (resonance = average) VSEPR structures predict 3‐dimensional arrangement of electron pairs in space Know and be able to predict 3D structure, sketch, including bond angles structures with these common geometries: linear, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramid, bent, trigonal bipyramid, octahedral, and square planar. Predict molecular polarity (dipole moment). Recall, in symmetrical structures any dipoles cancel out (non‐polar or zero dipole moment), while in asymmetrical structures any dipoles will sum (non‐zero dipole moment). Born‐Haber cycle and calculations