* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Financial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial
Survey
Document related concepts
International Financial Reporting Standards wikipedia , lookup
Derivative (finance) wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
European Union financial transaction tax wikipedia , lookup
Leveraged buyout wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis of 2007–2008 wikipedia , lookup
Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Patriot Act, Title III, Subtitle A wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Systemically important financial institution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
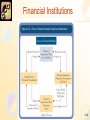
Chapter 3 Financial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial Institutions McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Financial Intermediaries Indirect Finance • An Institution stands between lender and borrower. Direct Finance • Borrowers and lenders deal directly with each other. 3-2 Financial and Economic Development 3-3 Financial Instruments • A financial instrument is the written legal obligation of one party to transfer something of value – usually money – to another party at some future date, under certain conditions, such as stocks, loans, or insurance. 3-4 Financial Instruments Serve as a: Means of payment (Like Money) Store of Value (Like Money) allow for the trading of risk 3-5 Financial Instruments Characteristics • • Standardization Communicate Information Classes of Financial Instruments • • Primary – underlying Instruments Derivative Instruments • Value derived from the behavior of Underlying instruments. 3-6 Value of Financial Instruments 1. 2. 3. 4. Size the promised payment. When the payment will be received. The likelihood the payment will be made (risk). The conditions under which the payment will be made. 3-7 Examples of Financial Instruments Primarily Stores of Value • • • • • Bank Loans Bonds Home Mortgages Stocks Asset-backed securities 3-8 Examples of Financial Instruments Primarily to transfer risk • Insurance • Futures Contracts • Options 3-9 Financial Markets Financial Markets are the places where financial instruments are bought and sold. 3-10 Financial Markets Role of Financial Markets. • Offer liquidity to borrowers and savers. • Pool and communicate Information. • Allow risk sharing 3-11 Financial Markets Structure of Financial Markets • Primary vs. Secondary Markets • Centralized Exchanges vs. Over-thecounter Markets. • Debt and Equity vs. Derivative Markets 3-12 Financial Markets Characteristics of a well-run financial market • Low transaction costs. • Information communicated must be accurate. • Investors must be protected. 3-13 Market Size and Investor Protection 3-14 Financial Institutions Role of Financial Institutions • Reduce transactions cost by specializing in the issuance of standardized securities • Reduce information costs of screening and monitoring borrowers. • Issue short term liabilities and purchase longterm loans. 3-15 Financial Institutions 3-16 Financial Institutions 3-17 Financial Institutions The structure of the financial industry • • • • • • Depository Institutions Insurance Companies Pension Funds Security Firms Finance Companies Government Sponsored Enterprises 3-18 Chapter 3 End of Chapter McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.