* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investing Options
Survey
Document related concepts
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Derivative (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Market sentiment wikipedia , lookup
2010 Flash Crash wikipedia , lookup
Day trading wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Short (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Securities fraud wikipedia , lookup
Stock valuation wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
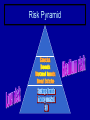
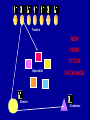
Investment Options Three reasons to invest • Investing helps beat inflation • Investing increases wealth • Investing is fun and challenging – Opportunity to take risk • Risk- the uncertainty of the outcome of any given situation – Gain knowledge 7 Wise practices of investing 1. Define your financial goals 2. Go slowly 1. Knowledge is power 2. If it sounds too good to be true it probably is 3. Follow through 4. Keep good records 5. Seek good investment advice 6. Keep knowledge current 7. Know your limits 1. How much money can you afford to risk? 2. How much risk are you willing to take? Risk/Reward The greater the potential reward – The greater the risk that must be taken in order to achieve it. Risk Reward Risk Pyramid Low risk/Low return • Government Savings Bonds • Certificates of Deposit • Savings/Money Market Accounts Risk Pyramid Medium risk/Medium return • Stock – Stock is a share of ownership in the assets and earnings of a company – core of America’s economic system • provide portfolio diversification • Diversification- spreading risk among many types of investments Why Companies Issue Stock • To grow or expand • To pay for ongoing business activities • It is popular because: – The company does not have to repay the money – Paying dividends is optional 2 Basic Types of Stock Common Stock Vs. Preferred Stock Common Stock • Common stock – shares or units of ownership in a public corporation – Most basic form of ownership – One vote per share owned to determine company’s board of directors Preferred Stock • Preferred stock – type of stock that pays a fixed dividend – Dividends • distribution of a portion of a company's earnings to shareholders – Fixed value paid out before common stock • IF company fails preferred gets paid before common – Less risk than common stock = lower returns – No voting rights How Well the Stock Market is Doing Overall Part 2 3 Basic Indicators • Dow Jones Industrial Average (“DOW”) – Lists the 30 leading industrial blue chip stocks • Standard and Poor’s 500 Composite Index – Covers market activity for 500 stocks – More accurate than DOW because it evaluates a greater variety of stock • National Association of Security Dealers Automated Quotations (“NASDAQ”) – Monitors fast moving technology companies – Speculative stocks, show dramatic ups and downs Ups and Downs • bull market -market is doing well – optimistic about the economy and are purchasing stocks • bear market -market is doing poorly – investors are not purchasing stocks – selling stocks already owned Purchasing Stock Stock brokers • Full-service brokers- most expensive – will call with advice – keep an eye on stock and call if changes need to be made. • Discount brokers- charge less – general advice – research options available – Buy and sell for you • Online brokerage sites- Cheapest – No advice-you do research for yourself – Order takers Three Stock Exchanges • New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) – Oldest and largest, began in 1792 – 2,800 companies – Strict requirements • American Stock Exchange – Began in 1849 – allowing younger, smaller companies to list • National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations – over the counter electronic market – 4,000 small companies – More volatile because companies are young and new Stock Transactions • Customer- you • Broker- qualified and regulated professional who buys and sells stocks • Trader- someone who buys and sells stock shares • Specialist- Seller of specific stock. Shows best bids and asked prices to the market during trading hours. Traders NEW YORK STOCK Specialist EXCHANGE Broker Customer The guaranteed way to make money in the stock market is simple: Buy Low and Sell High Medium Risk/Medium Return • Mutual funds- shares bought in a large, professionally managed group of investments – Pools money of investors to buy large amounts of stocks and bonds – Advantages • Professional management • Diversification- spreading risk among many types of investments Bond- money loaned to government or corporation – Corporate • Study Guide- read pages • Debenture 306-315 and • Mortgage 1.Explain the following types of bonds. • Convertible 2.Explain where and how – Government you can buy bonds. • Municipal 3.What are the three ways to • Revenue earn a return on a bond? • General 4.Why are bonds safer than obligation other investments? Risk Pyramid High Risk/High Return • Futures- buy and sell stock on a specific date in the future at a specific price – Betting the price will go up or down accordingly • Penny Stocks- low priced stocks of small companies- risk of failure is high • Collectibles- gain or lose value as public tastes change