* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Science - Petal School District
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
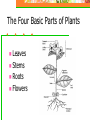
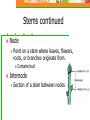
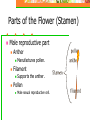
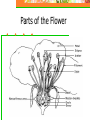
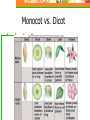
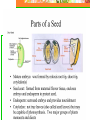
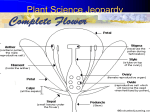
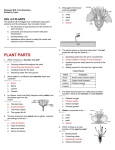
Unit 5: Plant Science Introduction to Agriscience Plant Science defined The application of scientific principles to the growth and management of plants. Agronomy – crops Forestry – trees Horticulture – ornamentals and fruits Floriculture – flowers Turf – grasses Parts of a Plant The Four Basic Parts of Plants Leaves Stems Roots Flowers Leaves Function Manufactures food for the plant by using light energy. (photosynthesis) Serves as site of respiration and transpiration. Useful for identification of the plant Margin (leaf edge) Shape Arrangement Leaves Stems Function Supports other plant parts such as…. Leaves Flowers Fruit Transports water and nutrients Two types of above ground stems Woody – hard with bark covering Herbaceous – soft with no bark Stems continued Node Point on a stem where leaves, flowers, roots, or branches originate from. Contains bud Internode Section of a stem between nodes Root Systems Function Anchor the plant Take in water & nutrients Hold soil Store food Types of roots Fibrous Tap Adventitious Fibrous Roots Primary root with many secondary branches Shallow roots ideal for water absorption (larger area) Most effective in controlling erosion Cause more damage to structures/utilities Tap Roots Continuation of primary root Ideal for anchorage Penetration is greater for water intake Can be used to store food Adventitious Roots Do not originate from the primary root Form on stems, branches, leaves, or old woody roots Include aerial and stilt roots Can form the largest part of the root system of some plants Roots Flowers Function Contain the sexual organs for the plant. Produce seeds & fruit. Attract insects with smell/color for pollination Parts of the Flower Sepals Outer covering of the flower bud. Protects the stamens and pistils when flower is in bud stage. Collectively known as the calyx. Parts of the Flower Petals Brightly colored Protects stamen & pistils. Attracts pollinating insects. (color) Collectively called the corolla. Parts of the Flower (Stamen) Male reproductive part Anther Filament Manufactures pollen. Supports the anther. Pollen Male sexual reproductive cell. Parts of the Flower (Pistil) Female reproductive part Ovary Enlarged portion at base of pistil. Produces ovules which develop into seeds. Stigma Usually “sticky” Receives the pollen. Parts of the Flower (Pistil) Style Connects the stigma with the ovary. Supports the stigma so that it can be pollinated. Pollen tube grows through toward ovary Nectaries Responsible for producing nectar which is composed mainly of sugars Internal – at the base of the pistil Insects/animals brush against reproductive parts for pollination External – on leaf stem, midrib, or margin Attracts predatory insects/animals Parts of the Flower Imperfect Flower Male or female reproductive organs, but not both. Example: A male flower has sepals, petals, and stamen, but no pistils. A female flower has sepals, petals, and pistils, but no stamen. Perfect Flowers Contains both male and female reproductive structures. Incomplete Flowers Missing one of the four major parts of the flower. Stamen Pistil Sepal Petal Complete Flowers Contains male and female reproductive organs along with petals and sepals. Flowers Imperfect flowers are always incomplete but…….. Perfect flowers are not always complete and…….. Complete flowers are always perfect. Groups of flowering plants Monocot Single cotyledon Flower parts in multiples of threes Leaf veins parallel Fibrous roots Vascular bundles scattered Groups of flowering plants Dicot Two cotyledons Flower parts in multiples of four or five Leaf veins branching Tap roots Vascular bundles in a ring Monocot vs. Dicot Pollination vs. Fertilization Pollination – the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma (allows fertilization to take place) Self pollination – when the pollen comes from the same flower or plant Cross pollination – when the pollen comes from a different plant Fertilization – union of the nuclei of the pollen and the nuclei of the ovule (produces seeds) Parts of a Seed Seed Coat Protects the seed. Sometimes very hard & difficult to germinate. Horticulturists assist germination by scarifying the seed coat or damaging the seed coat to promote germination. Stratifying seeds mimics the freeze/thaw cycle of nature. Parts of a Seed Endosperm Supplies food for the germinating seed. Embryo The young plant. Propagation Propagation What is Propagation? Increasing the number of a plant species or reproduction of a species. Two Types of Propagation Sexual Asexual Sexual Propagation The use of seed for reproducing plants. Allows the most variation of any propagation method. Only way to obtain new varieties and increase hybrid vigor of the plants. Less expensive & quicker than other methods. Occurs through pollination. Asexual Propagation Use of a part of a plant for reproducing new plants, other than the seed. (leaf, stem, root, tissue culture) Also called vegetative propagation. The new plant is an exact duplication of the parent plant. (same DNA) Methods of Asexual Propagation Cuttings Vegetative parts that the parent uses to regenerate itself. Examples: Leaf cuttings. Root cuttings. Stem cuttings. Root hormones are applied to speed up root development. Methods of Asexual Propagation Layering The stem is encouraged to root while still attached to the parent plant. Examples: Simple layering. Tip layering. Air layering. Methods of Asexual Propagation Division Dividing or separating the main part of the plant into smaller parts. Grafting Joining two plants together so they grow as one. T-Budding is the most common method. Methods of Asexual Propagation Tissue Culture Also called micropropagation. The use of a very small and actively growing part of the plant to produce a high number of new plants. Cloning achieved by tissue culture. Plant Life Cycles Annuals – complete life cycle in one season Warm season – spring and summer Cool season – fall and winter Biennial – complete life cycle in two years Vegetation produced the first year and fruit produced the second year Plant Life Cycles Perennial – live year after year Herbaceous – usually die back in winter and grow new vegetation each year Woody – do not die back because they withstand the colder temperatures Photosynthesis Photosynthesis Process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of a simple sugar (glucose). Chlorophyll & chloroplast are essential. Carbon dioxide is used to manufacture food for plant and releases oxygen necessary for animal life at the same time. Photosynthesis reaction Photosynthesis Rate of photosynthesis (food making) process depends on & varies with the…. Light intensity Temperature Concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon Dioxide Shortage of carbon dioxide causes a low rate of photosynthesis. Enclosed greenhouses can have a shortage of carbon dioxide. A CO2 generator might be used to correct a shortage of carbon dioxide in the greenhouse. Light Low light hinders plant growth. A dark room reduces the photosynthetic rate and plants will have stunted growth and yellow leaves. All plants have a preferred range, but they can adapt to various levels of light brightness (intensity). Temperature Affects the process of photosynthesis. Best rate of photosynthesis occurs between 65-85 degrees Fahrenheit. Extremes of temperature can completely stop the process. Respiration Respiration The process through which energy stored in organic molecules is released to do metabolic work Conducted in all living cells, it is controlled by enzymes, and releases carbon dioxide and water Respiration reaction Respiration Plants “breathe” through their leaves. The underside of the leaves have microscopic pores called stomata. Air passes in and out of the leaf through the stomata. Respiration takes place 24 hours a day. Each cell and the plant as a whole take in oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Transpiration Process in which excess water is given off by plants. Water escapes through stomata. Rate depends on light, temperature, humidity, wind, and water supply. Competition Process in which two organisms are trying to use the same resource. Water Space Sunlight Nutrients Competition Intraspecific – competition between organisms of the same species Interspecific – competition between organisms of different species Plant Nutrition Nutrients There are 16 chemical elements essential for plant growth and production. Divided into non-mineral and mineral classes and into macronutrient and micronutrient classes Nutrients Non-mineral – provided by air and water Mineral – provided by soil and fertilization Macronutrients – needed in large quantities for plant growth and production. Micronutrients – needed in small quantities for certain reactions within the plant such as hormone and chlorophyll production. Macronutrients (Air/Water) Carbon – C Hydrogen – H Oxygen - O Macronutrients (Soil) Nitrogen – N (major) Phosphorus – P (major) Potassium – K (major) Calcium – Ca (lime) Magnesium – Mg (lime) Sulfur - S Micronutrients Boron - B Copper - Cu Chloride - Cl Iron - Fe Zinc - Zn Manganese - Mn Molybdenum - Mo Fertilizers Fertilizers Complete fertilizer must contain the three nutrients. Nitrogen Phosphorus Potassium Fertilizers Come in various forms…. But most nutrients within a fertilizer must become in liquid form (soluble) to be used by plants. Organic Fertilizers Include animal manures & compost made with plant or animal products. Examples: Dried & pulverized manures. Bone Meal (4-12-0) Phosphorus is the primary element Soybean Meal (7-2-1) Blood Meal (12-0-0) Fertilizers Organic Fertilizers Usually slow acting and long lasting forms of nitrogen but lacking in the other primary nutrients. Except bone meal. Inorganic Fertilizers Have a higher analysis of soluble nutrients that have been blended together for a specific purpose. Fertilizer Application Broadcasting or spreading evenly over the entire surface is used on turf and home lawns. Side-dressing is done by placing fertilizer in bands about 8 inches from the row of growing plants. Foliar application is the spraying of fertilizer onto the leaves of plants. pH of Growing Media pH has the most impact on the availability of nutrients in the soil/media. pH Scale Ranges from 0 to 14. Indicates the level of acidity or alkalinity. 7 is considered neutral. Everything greater than 7 is considered alkaline (basic). Everything less than 7 is considered acidic. pH Scale pH Scale Amending the pH Alkaline soils can be made more acidic by lowering the pH value with sulfur or aluminum sulfate. Acidic soils can be made more alkaline by raising the value with lime. Lime usually applied as finely ground dolomitic limestone that supplies both calcium and magnesium. Other factors that affect plant growth and production Competition – when two plants are striving to get nutrients, water, sunlight, or space from one another. Insects – damage plants and fruit Climatic catastrophes – temperature, hurricanes, tornadoes, drought, flood, freeze Diseases – damage plants and fruit Growing Media Types of Growing Media Soil Top layer of the Earth’s surface. Primary medium for cultivated plants. Types of Growing Media Sphagnum Moss Used for encouraging root growth under certain conditions. Holds water well, but drains. Types of Growing Media Perlite Volcanic ash used for water adhesion and aeration in media mixes. Types of Growing Media Vermiculite A mineral; mica-type material used for water holding in media mixes. Types of Growing Media Peat Moss Used in media mixes of various types for water holding capacity and drainage. Types of Growing Media Bark Used in media mixes of various types for water retention, drainage, and aeration. Types of Growing Media Compost Decomposed organic matter, contains most nutrients needed by plants. Careers Floriculture Careers Related to flower production and use. Floriculture Careers Floral designer Flower grower Designs flowers for a florist or business. Produces flowers used in floral design. Greenhouse manager Manages the production process for a flower grower. Floriculture Careers Retail florist Floral business that furnishes flowers to the general public. Wholesale florist Floral business that furnishes flowers and supplies to a retail florist. Nursery/Landscape Careers Related to the use & production of plants for aesthetic purposes. Plants may be used around homes, businesses, parks, etc. Nursery/Landscape Careers Greenskeeper Landscaper Takes care of golf course turf. Installs plants in various locations. Landscape architect Design plans for plant installation. Nursery/Landscape Careers Nursery operator Grows trees and shrubs needed for landscaping. Turf farmer Grows turfgrass for sale. FFA Advisor High School