* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Currents and Climate
Survey
Document related concepts
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Diving in the Maldives wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
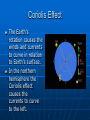
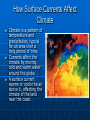
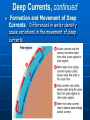
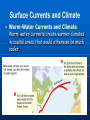
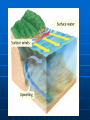
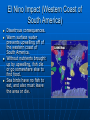
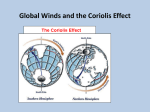
Currents and Climate Currents A current is a large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans. Currents carry water great distances and some currents move water at the surface of the ocean, while others move the deep water. Currents move the Sun’s energy from the equator to the poles. They also move cold water from the poles towards the equator. This moderates the climate of our planet. One Way to Explore Currents Norwegian explorer Thor Heyerdahl proved his theory that ocean currents influenced human migration by using a raft that was powered only by wind and ocean currents. He showed that Polynesia could have been settled from people migrating from South America. Surface Currents The wind mainly drives surface currents, which affects water to the depth of several hundred meters. If Earth were not rotating, winds and currents would only flow in straight lines to the north and south poles. This Coriolis effect causes the winds to curve. Coriolis Effect The Earth’s rotation causes the winds and currents to curve in relation to Earth’s surface. In the northern hemisphere the Coriolis effect causes the currents to curve to the left. The Gulf Stream The largest and most powerful surface current is the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is caused by strong winds from the west. The Gulf Stream carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to the Caribbean Sea, then northward along the coast of the United States. This current keeps Northern Europe much warmer in the winter than it would otherwise be. Ocean Current Map How Surface Currents Affect Climate Climate is a pattern of temperature and precipitation, typical for an area over a long period of time. Currents affect the climate by moving cold and warm water around the globe. A surface current warms or cools the air above it, affecting the climate of the land near the coast. Deep Currents Streamlike movements of ocean water located far below the surface are called deep currents. Deep currents are not controlled by wind. Deep currents form in parts of the ocean where water density increases. The density of the ocean is affected by temperature and salinity. Deep currents are caused by changes in density. Deep Currents, continued Formation and Movement of Deep Currents Differences in water density cause variations in the movement of deep currents. Surface Currents and Climate • Warm-Water Currents and Climate Warm-water currents create warmer climates in coastal areas that would otherwise be much cooler. Surface Currents and Climate, continued • Cold-Water Currents and Climate Cold-water currents keep climates along a coast cooler than the inland climate yearround. Surface Currents and Climate, continued Upwelling is the movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface of the ocean. The nutrients that are brought to the surface support the growth of plankton. Plankton support larger organisms, such as fish and seabirds. Upwelling is shown on the next slide. El Nino El Nino~an abnormal climate event that occurs every two to seven years in the Pacific Ocean. It begins when an unusual pattern of winds form over the western Pacific. Produces a change in the water temperature in the Pacific Ocean that produces a warm current. It can last one to two years. Effects of El Nino El Niño alters weather patterns enough to cause disasters, including flash floods, mudslides, and droughts. El Niño also prevents upwelling off the coast of South America. El Nino Impact (Western Coast of South America) Disastrous consequences. Warm surface water prevents upwelling off of the western coast of South America. Without nutrients brought up by upwelling, fish die or go somewhere else to find food. Sea birds have no fish to eat, and also must leave the area or die. El Nino Impact (On Land) Causes shifts in weather patterns around the world, bringing severe conditions to different areas. Unusually warm winter in northeastern U.S. Heavy rains, flooding, and mud slides in California. Deadly tornadoes in Florida. Studying & Predicting El Nino Learning as much as possible about El Niño is important because of its effects on organisms and land. To study El Niño, scientist use a network of buoys located along the equator. The buoys collect data about surface temperature, air temperature, currents, and wind. Forecasting El Nino Scientist don’t fully understand the conditions that create El Nino They can predict its occurrence by using computer models of the world climate Knowing when El Nino will strike, officials will give notice and can plan for unusual weather patterns. El Nino (2006 hurricane season) Why hasn’t there been many hurricanes in the 2006 hurricane season? The seasonal activity was lower than expected because of the rapid development of El Nino. This year there were only 9 named storms, 5 became hurricanes, and 2 became major hurricanes in Category 3 or higher. 2005 was the most active season on record, with 28 named storms, of which 15 became hurricanes. Five of the seven major storms hit the US, including Katrina.