* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology EOC Review Packet
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
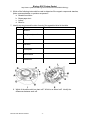
Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology Goal 1: Learner will develop abilities necessary to do and understand scientific inquiry. Goal 1 addresses scientific investigation. These objectives are an integral part of each of the other goals. 1. What is the scientific method? Give an example of how the scientific method has been used in a biological experiment. Identify and give a brief description of the following terms: * Hypotheses: * Variables: a. dependent b. independent * Control (or comparison) group: a. Why is it important to control the variables you are not testing? * Data collected and recorded: a. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? b. Give an example of each. * Charts and graphs: Be able to interpret these! * Analyze & interpret data: * Communicate findings: 2. How does a hypothesis become a theory? Give an example of how new information can change a theory. 3. What are some safety concerns for students working in the lab? Goal 2: Learner will develop an understanding of the physical, chemical and cellular basis of life. 4. What is the function and importance of each of the following organic molecules to organisms? Identify the subunits of each. a. Carbohydrates b. Proteins c. Lipids d. Nucleic Acids 5. Which type of organic molecule is each of the following compounds? a. Starch b. Cellulose c. Insulin d. Glycogen e. Glucose f. Enzyme g. Hemoglobin h. Fats i. DNA/RNA - BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -1- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 6. Which of the following tests could be used to determine if the organic compounds starches, lipids, monosaccharides, or proteins are present? a. Benedict’s solution b. Brown paper test c. Iodine d. Biuret’s 7. Identify the structure and function of each of the organelles listed in the table: Label Structure Function Nucleus Cell (plasma) membrane Cell wall Vacuoles Chloroplast Mitochondria Ribosomes 8. Which of the above cells is a plant cell? Which is an animal cell? Identify the differences between each cell. BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -2- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 9. Label the following parts of the microscope: eyepiece, course adjustment, fine adjustment, arm, objectives, stage, diaphragm, light source, base 10. Given the magnification of the eyepiece and the magnification of the objective, how can you determine total magnification? Example: Eyepiece is 10X and Objective is 40X. 11. What is the relationship between cells, tissues, organs and organ systems? 12. How do cells within an organism communicate with each other? What is the role of receptor proteins? What is the role of hormones within an organism? 13. What is homeostasis? How is it maintained in a cell? 14. What is osmosis? What controls osmosis? 15. What is the difference between active transport and passive transport (diffusion)? 16. In which direction would water move in the experimental setup in this diagram? = dissolved solute Semi-permeable membrane 17. What is ATP? What is it used for? How does it store energy? How does it release energy? 18. What are enzymes? BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -3- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 19. Enzymes are “re-usable” and “specific.” What do those two terms mean? 20. What factors affect how an enzyme works? 21. Photosynthesis: write the equation - what are the reactants and the products? 22. What is the purpose of photosynthesis? Where does it take place? Which living things perform photosynthesis? 23. Cellular respiration: write the equation - what are the reactants and the products? 24. What is the purpose of cellular respiration? Where does it take place? Which living things perform cellular respiration? 25. List factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis and respiration. 26. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? 27. What are the 2 types of fermentation? When or why would fermentation take place? Goal 3: Learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of life and the changes of organisms over time. 28. What is DNA? RNA? How are they similar? How are they different? 29. Draw and label the double helix structure. 30. What does the sequence of nucleotides in DNA code for? 31. What kinds of bonds hold the nitrogen bases together? 32. How do the nitrogen bases pair up? 33. What is DNA replication? When & where does it take place? 34. Explain how replication makes a new DNA molecule that is made up of one strand of “old” DNA and one strand of “new” DNA. 35. What are mutations? 36. What is transcription? Where does it take place? 37. Name the 3 types of RNA and describe the function of each. 38. What is translation? Where does translation take place? 39. What is a codon? What information does the codon provide? Be able to use a codon chart. 40. If given the DNA sequence: ATG TCA TTC TGA What is the mRNA sequence? What is the amino acid sequence? 41. How is it possible that most of an organism’s cells have the same DNA but perform different functions within the organism? 42. Compare and contrast mitosis & meiosis: Mitosis Meiosis What is the purpose? How many divisions? How many cells are produced? How does the chromosome number change? In what cells does it occur Asexual/Sexual reproduction BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -4- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 43. Put the following diagrams of mitosis in order: 44. Where are chromosomes found in a cell? Where are genes found? 45. How are homologous chromosomes alike? How are they different? 46. Define the following sources of variation and tell where each can occur in the cell cycle: crossing over, random assortment of chromosomes, gene mutation, nondisjunction, fertilization. 47. Who is Gregor Mendel? What did he do? 48. State the following: a. Rule of Dominance: b. Law of Segregation: c. Law of Independent Assortment: 49. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? 50. What determines the phenotype of an organism? Is it based on the genotype alone? 51. The gene for tall pea plants (T) is dominant. The gene for short pea plants (t) is recessive. A heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a short pea plant. What are the genotypes of the parent plants? 52. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring of this cross (#51)? Use a Punnett square to show your work. 53. Be able to solve and interpret problems featuring monohybrid crosses. (Parent, F1, F2 generations) 54. What is a karotype? How can gender or chromosomal abnormalities be determined by a karyotype? 55. Discuss these patterns of inheritance and give an example of each. Be able to solve and interpret crosses using Punnett squares. a. simple recessive heredity b. simple dominant heredity c. incomplete dominance d. codominance e. multiple alleles f. sex-linked inheritance g. polygenic traits 56. How can you use a test cross to determine the genotype of an organism? BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -5- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 57. Briefly describe the genetic cause of these conditions a. Sickle cell anemia b. Colorblindness c. Cystic fibrosis d. Hemophilia e. Down syndrome f. Huntington’s disease 58. Draw a pedigree of your fictional family showing the trait of having a white forelock of hair just above the forehead. Grandfather had the white forelock trait. Grandmother did not. Two of his children, your Uncle Bob and your mother, inherited the trait. His other child, your Aunt Joan, did not inherit the trait. Three grandchildren have the trait, and two do not. Aunt Joan never got married and never had children. Your dad does not have a white forelock of hair, but your older sister and brother do. You don’t, yet. Out of Uncle Bob’s children, Cousin Sue has a white forelock and Cousin Sally does not. After you draw the pedigree, make a hypothesis about whether the trait is dominant or recessive. What are your chances of having a white forelock of hair when you get older? 59. What were the reasons for establishing the human genome project? How can the project help to determine if an individual carries genes for a genetic condition? How can it help develop gene therapy? 60. Explain how gel electrophoresis separates molecules based on size. 61. What is DNA fingerprinting? What are some useful applications of DNA fingerprinting? 62. What is a transgenic organism? Explain how transgenic plants, animals and bacteria can be useful in both agriculture and the pharmaceutical industry. 63. What are some ethical issues associated with the study of genomics and biotechnology (like stem cell research and genetically modified organisms)? 64. Give a brief explanation for each of these Origin of Life theories and experiments: a. Spontaneous generation b. Louis Pasteur’s experiments c. Biogenesis d. Miller & Urey’s experiments e. Endosymbiont theory 65. How did early earth’s atmosphere affect the type of organisms that developed (anaerobic and prokaryotic)? 66. Define the theory of evolution by natural selection. Discuss Darwin’s contribution to this theory. Use these terms or concepts in your paragraph: variation, inherited traits, adaptation, environment, survive, reproduce, competition or struggle, common, descent or descended. 67. Explain how the evidence for evolution helps to explain the theory: a. Fossil record *What is the difference between relative and absolute dating methods? b. Shared anatomical structures c. Biochemical similarities 68. How do variations provide material for natural selection? What role does the environment play in selecting adaptations? BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -6- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 69. Speciation is the development of new species through evolution. What is the role of geographical isolation in speciation? 70. Give an example of natural selection occurring in the world today using resistance to antibiotics and pesticides. Goal 4: Learner will develop an understanding of the unity and diversity of life. 71. The original classification system began with just plants and animals. What has allowed for the expansion of the classification system to currently include 3 Domains and 6 kingdoms? 72. Linnaeus was the first to use binomial nomenclature (two-name naming system). Why is it important that the system exists? What language is used? What are the rules for writing a scientific name? For the name Homo sapiens: a. the first name, Homo, is the __________ b. the second name, sapiens, is the __________ 73. List the taxonomy rankings in order from the largest, broadest grouping (Kingdom) to the smallest, most specific grouping (species). 74. Explain how our current classification system uses the following evidence: a. evolutionary phylogeny b. DNA and biochemical analysis c. Embryology (study of embryonic development) d. Morphology (study of the shape and form of an organism) 75. Know how to interpret a cladogram (phylogenetic tree). 76. Fill in the chart below. Cell type Same Different Prokaryotic Eukaryotic 77. Fill in the chart below. Note similarities and differences between the Kingdoms. Eukaryotic Cell Structures Uni vs Nutrition Reproduction Kingdom Multicellular Protist Fungi Plant Animal 78. What is a dichotomous key? How is it used? Be able to use one. BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -7- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology 79. Compare and contrast how these organisms accomplish the essential life functions. Unicellular Annelids Insects Amphib- Mammals NonGymnoProtists ians vascular sperms Plants Transport Angiosperms Excretion Regulation Respiration Nutrition Synthesis Reproduction Growth & Development Transport - How organisms get what they need to cells; how they move waste from cells to organs of excretion. Excretion - How organisms get rid of their waste and balance their fluids (pH, salt concentration, water.) Regulation - How organisms control processes - hormones, nervous system. Respiration - How organisms get oxygen from the environment and release carbon dioxide back to the environment and how plants exchange gases. Nutrition - How organisms break down and absorb foods. Synthesis - How organisms build necessary molecules. Reproduction - Sexual vs. asexual, eggs, seeds, spores, placental, types of fertilization. Growth & development - metamorphosis, development in egg or in uterus, growth from seed or spore. 80. Using the organisms in the chart above, describe the following adaptations for each: a. feeding b. successful reproduction c. life on land 81. How have angiosperms and their pollinators been part of a co-evolutionary process? 82. What is the structure of a virus? 83. What is a pathogen? Describe each of the following pathogenic agents (viruses & bacteria): a. HIV b. Influenza BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -8- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology c. Smallpox d. Streptococcus (strep throat) 84. What is the interactive role of genetics and the environment in each of the following? a. sickle cell anemia and malaria b. lung/mouth cancer and tobacco use c. skin cancer, vitamin D, folic acid and sun exposure d. diabetes (diet/exercise and genetic interaction) e. PKU and diet 85. What is the purpose of the immune response? Identify the function of each of the following: a. T-cells b. B-cells *memory cells c. antibodies 86. Compare and contrast passive and active immunity. 87. What is a vaccine? How does it work? 88. How can nutrition have an effect on optimal health? 89. Plasmodium is a malarial parasite. How is it transmitted to humans? What are the symptoms and treatments for malaria? 90. How can lead and mercury be considered environmental toxins? 91. What is the difference between innate, learned and social behavior? 92. Determine what type of behavior each of the following is and briefly describe each. Innate/Learned/Social Description Behavior Suckling animal taxis (ex: moving away from or towards light) Migration estivation/hibernation Habituation Imprinting classical conditioning trial and error pheromone communication BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET -9- Biology EOC Review Packet http://www.ncpublicschools.org/curriculum/science/scos/2004/23biology courtship dances territorial defense Goal 5: Learner will develop an understanding of the ecological relationships among organisms. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. What is the relationship between organisms, populations, communities and ecosystems? Explain how abiotic and biotic factors are related to one another and their importance in ecosystems. What is symbiosis? Describe the following symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalisms, and parasitism. What is a predator/prey relationship? What is carrying capacity? How can limiting factors (food availability, competition, harsh winters) influence carrying capacity? Be able to interpret population growth graphs. What is exponential growth (J-curve)? What is logistic growth (S-curve)? Describe the relationship of the carbon cycle to photosynthesis and respiration. Draw a food chain and label the organisms: producer, consumer, herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, decomposer. Explain the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Include terms such as trophic-level, food web, and energy pyramid. What do human population growth graphs tell us about historical and potential changes? Explain how each of the following factors effect human populations: birth rate, death rate, population size, density and resource use on the environment. How does a change in the human population affect populations of other organisms? Explain how each of the following human activities impact local ecosystems: acid rain, habitat destruction, and introduction of non-native species. How do the greenhouse effect and natural environmental processes (e.g. volcanoes) influence climate? Relate the carbon cycle and human impact on atmospheric carbon dioxide. Humans do not always have a direct impact on natural resources. What are some indirect impacts of deforestation, pesticide use and bioaccumulation? What is a sustainable practice? Give an example. BIOLOGY EOC REVIEW PACKET - 10 -