* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRACTICE Final Exam: MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
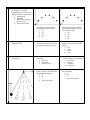
Name _________________________________ PRACTICE Final Exam: MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS Conceptual Physics Equations For objects moving at a constant speed: Distance = speed x time Average velocity or speed = Distance / Time Slope of a line = Δy/Δx = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1) 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 = 𝑚𝑎 𝑎= or 𝐹𝑛𝑒𝑡 𝑚 Weight = Fg = mg Acceleration due to gravity = g = 9.8 m/s2 Momentum p = mv Kinetic Energy KE = ½ mv2 Potential Energy Units 1 kilometer = 1,000 meters 1 meter = 100 cm 1 meter = 1,000 mm PE = mgh Name _______________________________ Conceptual Physics Final Exam Column A Mass is measured in units of: a. Kilograms b. Mass c. Newtons d. meters / second Column A Force is measured in units of: a. Kilograms b. Mass c. Newtons d. meters / second Column C Speed is measured in units of: a. Kilograms b. Mass c. Newtons d. meters / second 2. A force of 100 Newtons is exerted on a 10 kg object. What is the object’s acceleration? a. 0.10 m/s2 b. 10 m/s2 c. 100 m/s2 d. 1000 m/s2 A force of 100 Newtons is exerted on a 100 kg object. What is the object’s acceleration? a. 1 m/s2 b. 10 m/s2 c. 100 m/s2 d. 10,000 m/s2 A force of 100 Newtons is exerted on a 100 kg object. If you increase the force, the acceleration? a. increases b. stays the same c. decreases 3. What is the equation for average speed? 4. Speed is: a. The change in position per unit time b. The change in velocity per unit time c. The time it takes to go a certain distance 5. All objects on earth experience which force: a. Gravitational force b. Acceleration c. Mass d. Normal A falling object feels which forces (pick all that apply) a. Gravitational force b. Air resistance c. Normal d. Thrust 6. An object gains kinetic energy if it: a. Speeds up b. Is raised above the ground c. Slows down d. Is lowered closer towards the ground An object gains potential energy if it: a. Speeds up b. Is raised above the ground c. Slows down d. Is lowered closer towards the ground 1. A car’s speedometer shows its: a. Instant speed b. Average speed c. Instant acceleration d. Average acceleration Acceleration is: a. The change in position per unit time b. The change in velocity per unit time c. The speed of a moving object d. The time it takes to go a certain distance What is the average speed for the runner who runs 100 meters run in 50 seconds? a. 0.5 m/s b. 2 m/s c. 5000 m/s d. 2 hours Velocity is: a. The change in position per unit time b. The change in velocity per unit time c. The time it takes to go a certain distance All dropped objects have the same: a. Acceleration b. Gravitational force c. Mass d. Air resistance 7. Column A A proton has a ____ charge a. Positive b. Negative c. Neutral Column A An electron has a ____ charge: a. Positive b. Negative c. Neutral 8. An elevator is moving upwards at a constant speed. The velocity of the elevator is: a. Downwards b. Zero c. Upwards An elevator is moving upwards at a constant speed. The acceleration of the elevator is: a. Downwards b. Zero c. Upwards 9. You walk 10 steps to the east and 4 steps west. The total DISTANCE you traveled is: a. 6 steps b. 4 steps c. 14 steps d. 10 steps You walk 10 steps to the east and 4 steps west. The total DISPLACEMENT you traveled is: a. 6 steps b. 4 steps c. 14 steps d. 10 steps 10. Which of the Distance-vs-Time graphs below shows an object that is moving at a constant speed? Which of the Distance-vs-Time graphs below shows an object that is speeding up? A All dropped objects (ignore air resistance) and projectiles have a constant (aka the same): a. Force b. Acceleration c. Velocity d. Mass B C The acceleration of a falling object (ignore air resistance) is always 11. a. b. c. d. 9.8 N 9.8 m/s2 9.8 m/s 9.8 kg Column C Electricity is caused by the movement of what kind of charges: a. Positive (Protons) b. Neutral (Neutrons) c. Negative (Electrons) An elevator is moving upwards at a constant speed. The net force of the elevator is: a. Downwards b. Zero c. Upwards Which of the Distance-vs-Time graphs below shows an object that is stopped? D The velocity of falling object (ignore air resistance) will: a. Increase b. Decrease c. Remain constant 12. Column A A bowling ball and a golf ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber (ignore air resistance). Which one hits the ground first? a. Bowling ball b. Golf ball c. Both hit the ground at the same time d. Neither object falls Column A Column C You shoot a projectile. Which launch angle travels furthest? a. 10o b. 35o c. 45o d. 90o You shoot a projectile. Which launch angles remains in the air for the longest time? a. 10o b. 35o c. 45o d. 90o 13. What is the equation for potential energy? What is the value of “g” in the equation to the left? (Note, this is the acceleration due to gravity.) A 2 kg bowling ball is lifted to a height of 10 meters. Its potential energy is: a. 20 J b. 19.6 J c. 100 J d. 196 J 14. What is the equation for momentum? As a car speeds up, the car’s momentum: a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same A 5 kg cart is moving at a speed of 10 m/s. What is its momentum? a. 0.5 kg m/s b. 2 kg m/s c. 50 kg m/s d. 250 kg m/s A pendulum is swinging, as shown to the left. At which point is the pendulum stopped? a. A b. B c. C d. Same at all points At which point is the pendulum moving fastest? a. A b. B c. C d. Same at all points 15. A B C 16. 17. Column A (See above) At which point does the pendulum have the most Potential Energy? a. A b. B c. C d. Same at all points What is the equation for kinetic energy? 18. Column A (See above) At which point is does the pendulum have the least PE? a. A b. B c. C d. Same at all points What is the kinetic energy of 5 kg object moving at 10 m/s? a. 0.5 J b. 2 J c. 50 J d. 250 J Column C (See above) At which point does the pendulum have the most kinetic energy? a. A b. B c. C d. Same at all points A 5 kg block is moving at 10 m/s. Over time, it slows down due to friction. As it loses energy of motion, this energy becomes: a. b. c. d. Heat / Internal Energy Kinetic energy Potential energy Nuclear energy In the picture to the left, draw FOUR arrows to indicate the path of the ball if it’s released at points A, B, C and D. 19. What force keeps the moon in motion around the Earth? a. Electrostatic b. Gravitational c. Normal d. Tension You swing a ball attached to a string in a circle. Which force keeps the ball moving in a circle? a. Electrostatic b. Gravitational c. Normal d. Tension 20. Use the sketch of the roller coaster. At which point on the drawing does the rider have the most potential energy? At which point on the drawing does the rider have the least potential energy? A object in circular motion has a force towards: a. Center of circle b. Outwards c. In direction of velocity d. No force