* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Species Interactions - Colquitt County High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Drought refuge wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
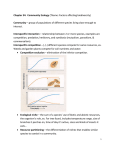
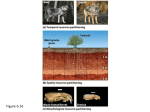
\ CHAPTER 41: SPECIES INTERACTIONS 1. Define community. Concept 41.1 – Interactions within a community may help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved. 2. Define interspecific interactions. 3. Ecological interactions can be grouped into three broad categories: competition, exploitation, and positive interactions. Complete the following table. Interaction Competition (-/-) Exploitation (+/-) Predation Herbivory Parasitism Positive interactions (+/+ or +/0) Mutualism (+/+) Commensalism (+/0) Description Example 4. Explain how competition contributes to competitive exclusion, resource partitioning, and character displacement. Concept 41.2 – Diversity and trophic structure characterize biological communities. 5. What is species diversity? What are its two components? Why is it important? 6. Define trophic structure. 7. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which provides a more “full” ecological picture and why? 8. Know the levels of trophic structure in food chains. Give a food chain here, including four links that might be found in a prairie community, and tell the level for each organism. 9. How is a keystone species different from a dominant species? 10. Compare and contrast the bottom-up model with the top-down model. Concept 41.3 – Disturbance influences species diversity and composition. 11. Define disturbance. 12. What is the intermediate disturbance hypothesis? Give an example of a disturbance event, and explain the effect it has on the community. 13. Ecological succession is the changes in species that occupy an area after disturbance. What is the difference between primary succession and secondary succession? 14. Describe how humans have impacted disturbance. Concept 41.4 – Biogeographic factors affect community diversity. 15. Describe how the latitude of a community and the area it occupies contribute to the tremendous range of diversity in biological communities. Concept 41.5 – Pathogens alter community structure locally and globally. 16. Describe the role pathogens play in structuring terrestrial and marine communities.