* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download solutions - Brock physics
Survey
Document related concepts
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
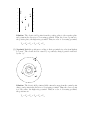
BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 1: January 2015 Course: PHYS 1P22/1P92 Examination date: 24 January 2015 Time of Examination: 11:00–11:50 Number of pages: 5 + formula sheet Number of students: 107 Instructor: S. D’Agostino No aids are permitted except for a non-programmable, non-graphics calculator. Solve all problems in the space provided. Total number of marks: 20 SOLUTIONS 1. [4 points] A parallel-plate capacitor has a capacitance of 7.0 µF when filled with a dielectric. The area of each plate is 1.5 m2 and the separation between the plates is 1.0 × 10−5 m. Determine the dielectric constant of the dielectric in the capacitor. Solution: κε0 A d Cd κ= ε0 A (7.0 × 10−6 )(1.0 × 10−5 ) κ= (8.85 × 10−12 )(1.5) κ = 5.3 C= 2. [4 points] The drawing shows an electron entering the lower left side of a parallel plate capacitor and exiting at the upper right side. The initial speed of the electron is 7.00×106 m/s. The capacitor is 2.00 cm long, and its plates are separated by 0.150 cm. Assume that the electric field between the plates is uniform everywhere and determine its magnitude. Solution: A full solution is contained at the end of the Chapter 18 lecture notes. The result is that the magnitude of the electric field is 2100 N/C. Be aware of an important rounding issue that came up in some students’ work on this problem. Read the full solution in the lecture notes for an explanation of this issue. C ~v1 6. 3 m m A 3.5 mm 3. [4 marks] Particle A has positive charge 3.2 nC and is fixed in place. Particle B has positive charge 8.3 nC and is also fixed in place. Particle C has positive charge 5.9 nC, is initially located as indicated in the figure, has initial speed 5.3 km/s, and has mass 9.4 × 10−12 kg. m 4.3 m B (a) Determine the electric potential at the initial position of Particle C. (b) Determine the initial electric potential energy of Particle C. (c) Determine the speed of Particle C when it is far from Particles A and B. Solution: A full solution is contained at the end of the Chapter 19 lecture notes. The results are: (a) 1.9 × 104 V (b) 1.1 × 10−4 J (c) 7.2 km/s 4. Answer each question briefly and clearly, in at most a few sentences. Your explanation may include formulas or diagrams, if you wish. Remember, brevity and clarity are courtesy. (a) [2 points] You have three metal rods with identical size, shape, and composition. Rod A has a charge of +6 units, and Rods B and C are neutral. Explain how to get a negative charge on one of the rods using only the three rods present. Solution: Place Rods B and C in contact. Bring Rod A close to, but not touching, Rod B. This causes negative charge to flow from Rod C to Rod B. While Rod A is still close, separate Rods B and C, leaving a negative charge on Rod B and positive charges on Rods A and C. This works provided that all the rods are insulated from the environment during the process. (b) [2 points] Some long-distance transport trucks have metal strips attached to them that drag along the road. Explain their purpose. Solution: Rubbing between tires and road may allow large charges to build up on the truck after a long journey. Then when the driver steps out of the truck, while holding on to the metal frame, a large spark may occur, which could set flammable contents of the truck afire. The metal strip prevents charge buildup on the truck by discharging continuously. (c) [2 points] Rank the positions according to their potentials, in order from highest to lowest. The electric field is uniform. − − + A + B − C − − + D + E − F − + + + − + Solution: The electric field points from the positive plate to the negative plate and points in the direction of decreasing potential. Thus, the closer a point is to the positive plate, the higher its potential. Thus, in order of decreasing potential, VB > VE > VC = VF > VD > VA (d) [2 points] Rank the positions according to their potentials, in order from highest to lowest. The electric field is caused by a positively charged particle indicated by the “⊕”. A B ⊕ C D F E Solution: The electric field points radially outwards, away from the central point charge, and points in the direction of decreasing potential. Thus, the closer a point is to the centre, the higher its potential. Thus, in order of decreasing potential, the positions are VC = VD > VF > VE > VB > VA