* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide Chapter 11 – Introduction to Atoms
Survey
Document related concepts
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
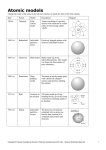
Study Guide Chapter 11 Atom – the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Dalton – developed the first modern atomic theory Thomson – discovered there are small particles inside the atom called electrons A. Plum pudding model – electrons mixed throughout the atom Rutherford – discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a dense, positive nucleus A. Rutherford model – dense nucleus with electrons surrounding at a distance Nucleus – an atom’s central region, which is made up of protons and neutrons Bohr’s model – electrons move around the nucleus in certain paths called energy levels Electron cloud model – (model theory) a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found Protons – positively charged particles in the nucleus Neutrons – particles of the nucleus that have no charge Electrons – negatively charge particles found around the nucleus in electron clouds Ion – if the charges are not equal between protons and electrons, you have a charged particle Atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotope – atoms that have the same number of protons but have different number numbers of neutrons Radioactive – an isotope that is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time Mass number – the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Atomic mass – the weighted average of the masses of natural isotopes of an element Forces in the atom A. Gravitational Force – pulls objects towards each other B. Electromagnetic force – opposite charges attract and same charges repel 1. force that holds electrons around the nucleus C. Strong Force – keeps a nucleus with 2 or more protons from flying apart D. Weak Force – allows a neutron to change into a proton or electrons in certain unstable atoms