* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
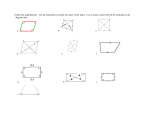
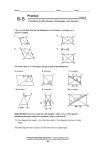
Download Proving Quadrilaterals Scaffolded WS
Survey
Document related concepts
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Group action wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Tensors in curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
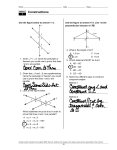
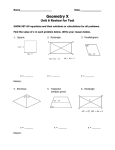
CC Coordinate Algebra Unit 6 – Connecting Algebra and Geometry Though Coordinates Proving Quadrilaterals Quadrilateral ABCD has the vertices: A(8, 7), B(12, 4), C(5, -2), D(1, 1) Definition: A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of opposite sides that parallel. 1. What formula do we use to show sides are parallel? 2. Plot and label the figure. Name 2 pairs of opposite sides. 3. Show with mathematical calculations that these opposite sides are parallel to prove ABCD is a parallelogram. Parallelogram EFGH has vertices: E(-12, -4), F(-4, 4), G(-7, 7), H(-15, -1) Theorem – Both pairs of opposite sides in a parallelogram are congruent. 4. What formula do we use to show sides are congruent? 5. Plot and label the figure. Name 2 pairs of opposite sides. 6. Show with mathematical calculations that these opposite sides are congruent to prove EFGH is a parallelogram. 7. Calculate the perimeter of Parallelogram EFGH. 8. Calculate the area of Parallelogram EFGH. CC Coordinate Algebra Unit 6 – Connecting Algebra and Geometry Though Coordinates Rectangle EFGH has vertices: E(-12, -4), F(-4, 4), G(-7, 7), H(-15, -1) Theorem – Both diagonals in a rectangle are congruent. 9. What formula do we use to show sides are congruent? 10. Plot and label the figure. Name 1 pair of diagonals. 11. Show with mathematical calculations that these diagonals are congruent to prove EFGH is a rectangle. Rectangle EFGH has vertices: E(-12, -4), F(-4, 4), G(-7, 7), H(-15, -1) Theorem – A rectangle has 4 right angles. 12. What kind of lines make right angles? What formula do we use to show these types of lines? 13. Plot and label the figure. Name all four sides. 14. Show with mathematical calculations that adjacent sides make right angles to prove EFGH is a rectangle. Rhombus JKLM has vertices: J(25, 14), K(15, 14), L(7, 8), M(17, 8) Theorem – The diagonals in a rhombus are perpendicular. 15. What formula do we use to prove perpendicular lines? 16. Plot and label the figure. Name the two diagonals. 17. Show with mathematical calculations that the diagonals are perpendicular to prove JKLM is a Rhombus.