* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Use core knowledge to give reasons for genetic variation and change.
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
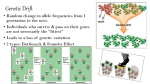
1 2 3 4 Recognise evolution as a process of change in allele frequency within a population. Description indicates there is a permanent change in the gene pool of the population over a period of time. Definitions include Gene, Allele, Species, Population, Gene Pool, Gene Flow, Allele Frequency. Describe the key ideas that are Key Darwinian ideas: used to formulate the theory of Heritable variation in populations (genes/alleles) evolution. Tendency of population to overproduce Competition in populations i.e. limited resources Survival linked to characteristics that are selected for (Natural Selection) Definitions including fitness / selection pressure / adaptation Increased reproductive success in individuals with favourable characteristics. Identify sources of variation in Identified as genetic variation as a result of: a gene pool. sexual reproduction (meiosis) – crossing over; independent assortment; mutation Identify factors that lead to Define Genetic Equilibrium. change in a gene pool. Identified as immigration; mutation; natural selection; population size; genetic drift; mate selection AND environmental variation leading to selection. The basic concept of barriers to gene flow e.g. geographic, potentially leading to biological isolation and speciation. 5 6 7 8 In relation to genetic change, define the term natural selection and describe the different types. Definitions have following concepts: Natural Selection: Survival and differential reproductive success in individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment at a given time. Stabilising - favours middle range of adaptive phenotype Directional – favours one extreme of adaptive phenotype Disruptive – Favours both extremes of adaptive phenotype. In relation to genetic change, Definitions have following concepts: define the terms genetic drift, Genetic Drift: random change in allele frequency OR chance the founder effect and the loss of alleles from gene pool; most pronounced in small bottleneck effect. population. Bottleneck: severe reduction in gene pool diversity, followed by recovery of a population Founder: development of a population from a small number of individuals with a limited gene pool. Causes/consequences of genetic drift, founder effect and the bottleneck effect in relation to genetic biodiversity. Use core knowledge to give E.g. different selection pressures produce a change in allele reasons for genetic variation frequency in the local gene pool, due to changed reproductive and change. success of individuals with particular genotype. Show understanding of E.g. if two populations are isolated i.e. no gene flow, and there genetic variation and change are different selection pressures then the allele frequencies in by using the core knowledge each gene pool will diverge. Reasoning includes an explanation to link ideas e.g. in justifying, of survival of the fittest as appropriate to two different relating, evaluating, environments. e.g. Hedgehog qu (2004 exam). comparing and contrasting or analysing.













![Microevolution is a change in population`s gene pool [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000926710_1-bb56556ff16eaa56e5fbaa116b073962-150x150.png)