* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1 ATA for AP
Survey
Document related concepts
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Sharing economy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Consumerism wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
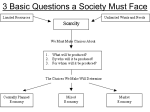
Name: __________________________________________ Date: _______________ Quiz name: Copy of Economics - Unit 1 Test - Honors (from version 1) 1. Any resources that are made by humans and used to create other goods and services are called A services. B production. C capital. D labor. 2. The resources used to make all goods and services are the A production possibilities. B factors of production. C production trade-offs. D opportunity costs. 3. The purpose of a production possibilities graph is to A enable a country to mobilize to win a war. B keep an economy from having nonproductive workers. C show alternative ways to use an economy’s resources. D make it possible to increase an economy’s output. 4. The opportunity cost of a decision can be examined by using a A production possibilities graph. B factors of production chart. C global trade-off grid. D graph of increasing costs. 5. Production possibilities frontiers curve when they are charted on a graph because they show A the underutilization of resources. B the maximum output of goods and services. C the increasing costs resulting in increasingly less output. D the technological level of the economy’s productivity. 6. 7. Why are all goods and services scarce? A Some goods cost more than others. B All resources are scarce. C Some things are needs and others are wants. D Some people want to have more goods than others. A country’s production possibilities increase because the available workers become more skilled at using a computer. This is an example of growth caused by Page 1 of 4 A global resources. B physical capital. C technology. D production opportunity. A nation’s automakers install new robotic machinery to build cars. Now, cars take only a day to make, and the factories can produce many more cars than before. This is an example of growth caused by 8. A land and natural resources. B human capital. C technology. D production possibility curves. 9. What can a decision-making grid do? A tell you the right course of action B show you every possible consequence of your decision C help you determine some of the opportunity costs for your decision D show you every possible benefit of your decision 10. One example of thinking at the margin is A determining whether it is better to spend your savings on a new CD player or on a television. B deciding whether the benefit of working two extra hours per day is worth the sacrifice of study time. C putting all of your money in a savings account because the interest rates are so high. D deciding to buy a car you don’t really like because it is significantly less expensive than the one you want. 11. Which of the following is NOT a key economic question? A What goods and services should be produced? B How should these goods and services be produced? C Who consumes these goods and services? D How should it be ensured that goods and services are paid for? 12. What incentive motivates a manufacturer to sell a product? A making profits on sales B putting others out of business C pleasing the consumer D popularity of the product 13. Which of the following was a free market philosopher? A Karl Marx B Adam Smith C Vladimir Lenin D Friedrich Engels 14. What incentive (reason) do manufacturers have to sell their products? A making profits on sales B pleasing the consumer Page 2 of 4 C putting others out of business D popularity of the product What might be a hardship for citizens of a centrally planned economy making a transition to a market-based system? 15. A Farmers would have to grow the crops that the government instructed them to. B Only poor quality goods would be available to consumers, because manufacturers focused on quantity, not quality. C Workers would lose job security and guaranteed incomes that they were used to under the old system. D Entrepreneurs would have fewer opportunities to start new businesses. 16. Which of the following does a government provide as part of a welfare safety net for the people? A general elections every four years B unemployment compensation C a strong military defense D regulation of commerce 17. Why do markets exist? A Markets ensure that government does not intervene in the production of goods and services. B Markets provide self-sufficient people with public places for the exchange of ideas. C Markets ensure economic equity for all people. D Markets allow people to buy what they need to consume and sell the specialized goods and services they produce. 18. Which of the following goals is difficult to achieve in a pure free market system? A economic efficiency B economic equity C economic freedom D economic growth A person believes that real social equality can only exist when political equality is coupled with economic equality. This person believes that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout society. This person is a 19. A socialist. B communist. C capitalist. D authoritarian. 20. Which of the following is NOT a weakness of centrally planned economies? A Most workers lack job security because they don’t have government jobs. B Consumers’ needs are generally not met. C Workers lack incentives to be innovative. D Individual freedoms are sacrificed for societal goals. 21. The economy of China is in transition. What does this mean? A Investments are determined by state control instead of by private decision. Page 3 of 4 B The economy is moving from central planning toward a market-based system. C Individual firms are in the process of being sold to the state. D The government rarely interferes in the free market and is highly receptive to foreign investment. 22. In which of the following lists of mixed economies does the market system dominate? A France, Canada, South Africa, United Kingdom B United States, United Kingdom, Singapore, Hong Kong C Cuba, Greece, China, United States D Russia, Peru, France, Canada Which of the following is a private organization that attempts to influence public officials to act or vote in ways that will benefit the group’s members? 23. A market research group B free enterprise group C public policy group D interest group 24. What is the difference between a business cycle and the day-to-day ups and downs of the market? A The day-to-day ups and downs of the market can be much more extreme than a business cycle, particularly when the road runner flees from Wile E. Coyote. B The day-to-day fluctuations are more likely to have an impact on people’s finances long-term, like when Justin Bieber forgets to pull up his pants. C A business cycle is usually more restricted to the United States, whereas market fluctuations are worldwide and cause extreme tsunamis. D A business cycle is a major, prolonged fluctuation rather than a day-to-day movement. 25. What effect does new technology usually have on an economy? A It makes the economy stronger and more efficient. B It reduces the dependence of the economy on business. C It slows an economy down for at least a while. Page 4 of 4