* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s 2 Law
Survey
Document related concepts
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
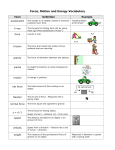
Newton’s nd 2 Law Chapter 11 – Section 2 Pages 316 – 322 in textbook Newton’s nd 2 Law of Motion DESCRIBES…. The net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration and its mass. One Equation…. The relationship between the quantities of force, mass, and acceleration can be written in one equation: Force = Mass x Acceleration F = ma Compare and Contrast Which shopping cart will be easier to push/move? How do the shopping carts relate to Newton’s 2nd Law? Answer: The empty shopping cart has less mass than the full shopping cart, therefore it will need a smaller force to accelerate it. Units: F = ma Mass units example: kg Acceleration units example: m/sec/sec Force units: kg * m/sec/sec ???? What a mess! Force is measured in units called the Newton (or N for short!) 1N = 1 kg x 1 m / sec / sec This equation says that one Newton equals the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second per second! Sample Problem #1 A bicycle has a mass of 40.0 kilograms. Suppose the bike accelerates at 1.0 m/s/s. Find the net force being exerted on the bicycle. Step 1: F = ma Step 2: F = 40.0 kg x 1.0 m/s/s Step 3: F = 40.0 N Sample Problem #2 A speedboat is pulling a 52,000 gram skier. The force causes her to accelerate at 2.0 m/s/s. Calculate the force. F = ma F = 52.0 kg x 2.0 m/s/s F = 104.0 kg m/s/s OR F = 104.0 N F M A Sample Problem #3 An object with a mass of 50 kg is pushed with a force of 150 Newtons. What is the objects acceleration? A = F/M A = 150 kg m/s/s / 50 kg A = 3 m/s/s or 3 m/s2 F M A Sample Problem #4 What is the mass of an object that accelerates at a rate of 5 m/s2 after a force of 100 N is applied to it? M = F/A M = 100 kg * m/s/s / 5 m/s/s M = 20 kg F M A GRAVITY! The force that pulls object’s to the center of the earth is known as gravity. Gravity attracts objects towards each other. Gravitational force decreases as: Distance increase between objects Masses of objects decrease. Law of Universal Gravitation Gravity is everywhere in the universe! The Law of Universal Gravitation states that the force of gravity acts between all objects in the universe! Acceleration due to GRAVITY Acceleration on the Earth due to gravity is 9.8 meters/second/second This means: For every second an object falls, it’s velocity increases by 9.8 m/s! Let’s figure it out……. A parachutist jumps from a plane. What is her acceleration due to gravity? Complete the below chart. Time 1.0 second 2.0 seconds 3.0 seconds 4.0 seconds Velocity 9.8 meters/second 19.6 meters/second 29.4 39.2 meters/second meters/second Weight The weight of an object is the size of the gravitational force exerted on an object. Since weight is a force, you can rewrite Newton’s second law of motion as W=ma. Since acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s2, you can rewrite the formula for weight as: W = m * 9.8 m/s2 Weight How much would a 50 kg person weigh on the surface of the earth? Force = Mass * Acceleration (due to gravity) Force (Weight) = 50 kg * 9.8 m/s2 Force (Weight) = 490 kg * m/s2 Force (Weight) = 490 Newtons Who Wins? Acorn or Leaf? Why does an oak leaf flutter straight to the ground yet an acorn will fall straight down? Answer – AIR RESISTANCE Air Resistance Air resistance is a form of friction that acts to slow down any object moving in the air. Air resistance increases as: 1. 2. The Surface area of the object increases The velocity of the object increases When the air resistance balances the force of gravity, the net force is zero, also called terminal velocity. In a vacuum, where there is no air, all objects fall with the same acceleration!