* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An
Survey
Document related concepts
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrodynamic tether wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electron paramagnetic resonance wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
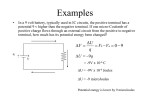
Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An electron moving parallel to the x-axis has an initial speed of 3.70×(10)^6 m/s at the origin. It's speed is reduced to 1.40×(10)^5 m/s at the point x=2c.m -calculate the electric potenial difference between the origin and that point? Find: vE – ? Given: v0=3.7×106 m/s v=1.4×105 m/s x=0.02 m e=-1.6×10-19 C m=9.1×10-31 kg Solution: The changing of the kinetic energy of electron: W= mv20 2 − mv2 2 (1), where m is the mass of electron The electric field performs work: A = Fx (2), where F is the electric forse, x is the displacement of electron Electric forse: F = vE |e| (3), where vE is the electric potenial, e is electron charge (3) in (2): A = vE |e|x (4) The changing of kinetic energy of electron is equal to work of electric field: mv20 2 − mv2 2 = vE |e|x (5) Of (5) vE = 2 mv2 0 −mv 2 2 |e|x (6) Of (6) vE=1.9×10-7 N/C Answer: 1.9×10-7 N/C Answer provided by https://www.AssignmentExpert.com



![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-150x150.png)