* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz 4 Solutions
Survey
Document related concepts
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
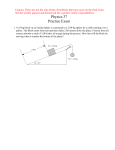
Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 April 17, 2009 Instructions Write your name, student ID and name of your TA instructor clearly on all sheets and fill your name and student ID on the bubble sheet. • Solve all multiple choice questions. No penalty is given for wrong answers. • Solve each problem on a different sheet of paper. You may write on the back of the problem sheets (please indicate “OVER” at bottom of the front so that the grader knows to check the back). • Solutions to the problems should begin from the following basic physical principles: – If ~r(t) is the position of the object as a function of time than velocity is ~v(t) = 2 acceleration is ~a(t) = ddt~2x . d~r dt and – When the acceleration is a constant ~a then~r(t) =~r0 +~v0t + 12~at 2 . – For motion in a circle of radius R, v = Rω, s = Rφ, and the centripetal acceleration is ac = ω2 R – Newton’s Laws: ~F = m~a and ~F12 = −~F21 – Common forces include static friction (F ≤ µs FN ), kinetic friction (F = µk FN ), gravitational force (F = mg), and the spring force (F = −kx). R – Kinetic energy is 1 mv2 , work is W = ~F · d~x , gravitational potential energy is Ug = 2 mgh, and spring potential energy is Us = 12 kx2 . – Rotational physics: K = 12 Iω2 , τ = Iα = Fr sin θrF , θ = θ0 + ω0t + 21 αt 2 , L = Iω. – Moments of inertia: I = ∑i mi R2i . For objects on axes through the center of mass: MR2 – hollow cylinder, 12 MR2 – solid 1 cylinder, 25 MR2 – solid sphere, 23 MR2 – hollow sphere, 12 ML2 – thin rod. For parallel axes: I = Ic m + Md 2 . • Show all steps in the derivation of the answers. Make sure you write neatly and orderly. It is YOUR RESPONSIBILITY to make sure that the grader understands your solution. S/he will not give full points if they can not follow the solution, even if the final answer is correct. • The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m/s2 . • The solutions to the quadratic equation 0 = ax2 + bx + c are given by x = • You can use a calculator. Page 1 √ −b± b2 −4ac . 2a Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 Page 2 April 17, 2009 Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 Last name : April 17, 2009 First name : Student id : TA : Problem 1 (25 points) Because of your physics background, you have been asked to help evaluate the safety preparations for new ethanol factory. Safety requirements stipulate that all fire doors must be able to be closed within 15 seconds of an alarm even without power to the building. The factory has a large loading area which can be closed by a large door 2.5 m high and 4 m wide weighing 2500 kg. You estimate that three loading dock staff could reach the door within 10 seconds, leaving 5 seconds to close the door. You estimate that each staff member can push with a force of 300 N and that they will need 1 m between each of them as they push on the door. The door, which has a moment of inertia of 1/3Mr2 around its hinges, needs to rotate 120 degrees for it to close completely. Does this arrangement meet the safety requirement if the stafff members position themselves optimally? The torque on the door will be: τ = τ1 + τ2 + τ3 = 4 m · 300 N + 3 m · 300 N + 2 m · 300 N = 2.7 kN · m This will generate an angular acceleration by τ = Iα. This torque will allow the door to rotate and we must determine the time for the door to rotate by 120o . φ = t = = = = Yes. This design meets the requirement. Page 3 1 2 αt 2 r 2φ α r 2φI τ r 2φMr2 3τ 4.5 s Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 Page 4 April 17, 2009 Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 Last name : April 17, 2009 First name : Student id : TA : Problem 2 (25 points) You have been hired to help set up a trade-show introduction for a new steamroller. The tradeshow is being held in a hall where the engine cannot be operated, so the artistic designer would like to have the steamroller roll down an incline and then across the stage at a stately 0.5 m/s and finally be stopped by large spring while having the rollers make a last quarter-rotation for dramatic effect. The steamroller consists of two thin steel cylinders rollers of radius 80 cm and mass 5000 kg (each) which function as the front and rear “tires” and a body containing the engine and cab which has a mass of 3000 kg. Your role is to determine the necessary height of the incline and the spring constant of the necessary stopping spring. You decide to neglect any effects of rolling friction in solving the problem – the axles on this new steamroller are very well made and the rollers will turn easily. This is an energy problem. As the steamroller crosses the stage, it will have a kinetic energy : K = = I = K = = 1 2 1 2 mv + Iω 2 2 1 2 1 v2 mv + I 2 2 2 R 2mc R2 1 (mb + 2mc )v2 + mc v2 2 1 (mb + 4mc )v2 = 2875 J 2 This energy must be provided by the incline: K = mgh = (mb + 2mc )gh h = 2.25 cm At the end of the process, the full energy will be absorbed by the spring while the wheels make a quarter turn. 1 2 kx 2 1 x = 2πR = 1.26 m 4 2K k = = 3640 N/m x2 Us = Page 5 Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 Page 6 April 17, 2009 Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 April 17, 2009 Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each) Question 1 : A playground merry-go-round with a radius of 2.0 m and a rotational inertia of 100 kgm2 is rotating at 3.0 rad/s. A child with a mass of 22 kg jumps onto the edge of the merry-goround, traveling radially inward. What is the new angular speed of the merry-go-round? A) 1.6 rad/s B) 1.2 rad/s C) 2.4 rad/s D) 2.0 rad/s E) 3.4 rad/s The correct answer is A. Question 2 : A 620-g object traveling at 2.1 m/s collides head-on with a 320-g object traveling in the opposite direction at 3.8 m/s. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the change in the kinetic energy of the 620-g object? A) B) C) D) E) It gains 0.69 J. It loses 0.23 J. It loses 0.47 J. It loses 1.4 J. The energy of the object is unchanged. The correct answer is B. Question 3 : A car is traveling at 20.0 m/s on tires with a diameter of 70.0 cm. The car slows to a rest after traveling for a half a minute. If the tires rolled without slipping, what was the magnitude of the average angular acceleration of the tires during the time the car slowed to a rest? A) B) C) D) E) 0.667 rad/s2 1.33 rad/s2 0.952 rad/s2 1.67 rad/s2 1.90 rad/s2 The correct answer is E. Page 7 (OVER) Quiz Number 4 PHYSICS 1301.100 April 17, 2009 Question 4 : A spherical water droplet of radius 0.200 cm is spinning uniformly with an angular velocity (10.0 rad/sk̂). A second spherical water droplet of radius 0.100 cm is spinning uniformly with angular velocity (20.0 rad/sî) . The two water droplets collide and form a new spherical water droplet. If the new droplet spins uniformly, what is its angular velocity? A) B) C) D) E) (0.818 rad/s)î + (6.67 rad/s)k̂ (0.514 rad/s)î + (8.22 rad/s)k̂ (0.441 rad/s)î + (9.81 rad/s)k̂ (0.725 rad/s)î + (7.92 rad/s)k̂ (0.697 rad/s)î + (7.51 rad/s)k̂ The correct answer is B. Question 5 : A 2.00-m rod of negligible mass connects two small objects. The mass of one object is 1.00 kg and the mass of the other is unknown. The center of mass of this system is on the rod a distance 1.60 m from the 1.00-kg mass object. What is the mass of the other object? A) 4.11 kg B) 3.22 kg C) 4.00 kg D) 0.250 kg E) 0.800 kg The correct answer is C. Page 8