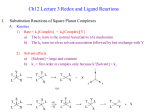
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry 212 Name:
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Halogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
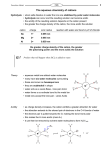
Chemistry 212 Key 5 Spring 2004 1. Which of the following is least likely to be colored? a) Co3+ b) Cr3+ c) Fe3+ d) Mn2+ e) V5+ 2. The reaction of CrBr3(H2O)5 with excess AgNO3 yields 1 mole of AgBr per mole of Cr. The best representation of this compound is: a) [Cr(H2O)5Br]Br2 b) [Cr(H2O)3Br2]Br•2H2O c) [Cr(H2O)4Br]Br2•H2O d) [Cr(H2O)2Br3]•3H2O 3. The formulae provided as answers to question 2, are examples of __________ isomers. c) linkage d) optical a) coordination sphere b) geometrical e) stereo 4. Which of the following elements exhibits a maximum oxidation state of +7? a) Ba b) Be c) Br d) Co e) O f) Se 5. Which of the following elements exhibits forms π-bonds most readily? a) Ba b) Be c) Br d) Co e) O f) Se 6. What is the VSEPR geometry of SF4? a) bent b) octahedral c) seesaw d) square planar e) trigonal bipyramidal 7. What mass of AgCl dissolves in 1.0 L of water? Ksp(AgCl) = 1.8 x 10-10 a) 2.6 x 10-8 g b) 1.3 x 10-5 g c) 1.9 x 10-3 g d) 12 g e) cannot determine from the information given 8. A certain chemical reaction has ∆H = -89 kJ/mol and ∆S = 55 J/mol•K. When does this reaction proceed spontaneously? a) The reaction is always spontaneous. b) The reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures. c) The reaction is spontaneous only at low temperatures. d) The reaction is never spontaneous. Discussion questions 1. Define: (8 points) complex – an assembly of a metal ion and bound Lewis bases electronegativity – the tendency of bound atoms to attract electrons towards themselves 2. Consider the high spin molecule trans-[Fe(NH3)4Cl2]Cl. What is the electron configuration of the Fe? Draw out the crystal field energy level diagram, show electron placement and label it. Draw the complex ion. (14 points) [Ar] 3d5 Cl H3N Fe H3N NH3 Cl NH3 Cl z2 ↑ ↑ x2-y2 ↑ ↑ ↑ xy yz xz 3. Describe how the d orbitals are split by ligands in a tetrahedral field. (8 points) Assume a metal with 1 electron in its d-orbitals and 4 ligands an infinite distance away centered between the coordinate axes in non-adjacent volumes (opposite corners on a cube). At this point the 5 d-orbitals are degenerate and the electron spends an equal length of time in each. As the ligands approach the metal, their lone pairs of electrons repel the metal delectron when it is in orbitals that point at the ligands (xy, xz, and yz). This raises the energy of these orbitals relative to the energies of the orbitals pointing along the axes (z2 and x2-y2). xy, xz, yz xy xz yz z2 x2-y2 ∆ z2 x2-y2 4. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium sulfide with hydrochloric acid? (5 points) Na2S(aq) + 2 HCl(aq) → 2 NaCl(aq) + H2S(g) 5. Discuss the halogens. (5 points) Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionization energies. Each is the highest of their respective period. All readily form the –1 ion. All possess the highest electronegativities of their respective periods. These properties, in conjunction with low X2 bond energies make these elements highly reactive. Beginning with chlorine, all can form compounds with the halogen in a positive oxidation state (+1, 3, 5, & 7). They all exist as colored diatomic molecules. 6. Complete and balance these reactions: (8 points) a) CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) b) NaNH2 (s) + H2O(l) → NaOH(aq) + NH3(aq) 7. Provide formulas for silicon dioxide, potassium phosphide, sodium thiosulfate (central sulfur). Give the oxidation state of the underlined atom for each. (12 points) SiO2 (+4) K3P (-3) Na2S2O3 (+6) 8. In a certain oxidation state, copper behaves as if it were a main group element instead of a transition metal. What oxidation state is that and why would you expect this to be observed. (5 points) Cu+, its electron configuration is [Ar] 4d10. This is the same as Zn2+ and leads to reactivity as the alkaline earth metals.