* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Survey
Document related concepts
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
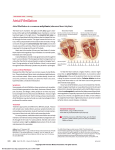
ΘΕΜΑ ΑΝΑΦΟΡΑΣ What is Atrial Fibrillation? Πηγή: Medical News Today The human heart has two upper chambers and two lower chambers. The upper chambers are called the left atrium and the right atrium - the plural of atrium is atria. The two lower chambers are the the left ventricle and theright ventricle. When the two upper chambers - the atria - contract at an excessively high rate, and in an irregular way, the patient has atrial fibrillation. The Three Types of Atrial Fibrillation • Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation - the abnormal electrical signals and quickened heart rate begin suddenly and then stop on their own. Patients may experience mild or severe symptoms. Symptoms can last for just a few seconds or minutes, or persist for hours, and even days. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation generally originates from the junction of the pulmonary veins within the left atrium (the left upper chamber of the heart). • Persistent Atrial Fibrillation - in this case the atrial fibrillation only stops when the patient receives treatment. • Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation - used to be called Permanent Atrial Fibrillation. The patient’s normal heart rhythm cannot be restored with the usual treatments. Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation can occur more frequently and eventually become Longstanding Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. The term atrial fibrillation comes from the Latin words atrium, meaning “hall”, fibrilla, meaning “small fiber”, and atio, meaning “process”. According to Medilexicon’s medical dictionary, atrial fibrillation is”fibrillation in which the normal rhythmic contractions of the cardiac atria are replaced by rapid irregular twitchings of the muscular wall; the ventricles respond irregularly to the dysrhythmic bombardment from the atria.” The most common type of arrhythmia Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia - problems with the speed or rhythm of the heartbeat. Arrhythmias are caused by a disorder in the heart’s electrical system. How does arrhythmia occur? The walls of the atria and ventricles are made of virtually 100% pure muscle. A heartbeat is caused by the tightening of these muscles. When the muscles tighten the chambers squeeze closed and push out the blood which is inside them. Heartbeat control begins with the sinoatrial node - a small clump of muscle cells located in the right atrium. This is the heart’s natural pacemaker; it sends electrical impulses to the atrioventricular node which exists between the atria and ventricles. The atrioventricular node determines how much the ventricles contract. Our pulse rate is caused by the contraction of the left ventricle. When the atrioventricular node receives too many impulses more than it is able to conduct - atrial fibrillation occurs. The result is irregular contractions of the ventricles. That is why a patient with atrial fibrillation has an irregular and high pulse rate. Put simply - during atrial fibrillation the contractions of the two upper chambers of the heart are not synchronized with the contractions of the two lower chambers. Atrial fibrillation is a rapid and irregular heart rate. It frequently causes poor blood flow to the body. Incidence of atrial fibrillation in the USA and Europe Atrial fibrillation currently affects almost 7 million people in the USA and Europe. Incidence is expected to double within the next forty years. [ 24 ] Vol 1, Issue 2 - 2015 (Year 11/60) What is Acute-onset atrial fibrillation? This is an atrial fibrillation that has started suddenly, or has made symptoms get worse. This could be a recent-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) - it has happened for the first time - or the patient may have had AF before. Acute-onset AF can occur in patients with either persistent or paroxysmal AF, and among those who are already undergoing AF treatment, as well as patients who are not being treated. Some patients with acute AF which leads to potentially dangerous symptoms may need treatment in hospital. What is Post-operative atrial fibrillation? This is a type of AF that may happen after surgery. Generally, it stops by itself. Sometimes the patient may require treatment. What are the Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation? Fast heartbeat - usually over 140 beats per minute. A patient can take his/her own pulse by placing a finger on the wrist or neck. The following signs and symptoms are also possible. Some of these signs and symptoms are similar to ones we experience when our heartbeat increases with vigorous physical exercise: • Dizziness. • Lightheadedness - lightheadedness differs from dizziness in medical terminology. A person with lightheadedness feels he/she is going to faint. • Confusion. • Palpitations - a racing, uncomfortable sensation in the chest. A flopping in the chest.