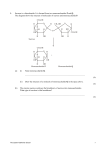
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download carbohydrates
Survey
Document related concepts
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
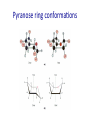
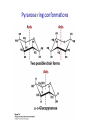
Chapter 7 CARBOHYDRATES Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is a carbohydrate? Monosaccharides Cycliza=on of monosaccharides Glycosidic linkages Common disaccharides Polysaccharides – Starch and glycogen – Cellulose and chi=n 7. Glycoproteins Ring conforma=ons • Configura)on vs. conforma)on • Furanose rings – Sugar pucker – C2-‐endo and C3-‐endo favored in nucleic acids Pseudorotational cycle for nucleoside furanose ring puckers. Maderia M et al. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007;35:1978-1991 © 2007 The Author(s) Ring conforma=ons • Configura)on vs. conforma)on • Furanose rings – Sugar pucker – C2-‐endo and C-‐3 endo favored in nucleic acids • Pyranose rings – Chair and boat conforma=ons – Chair is more stable (crowding at axial posi=ons in boat form) Pyranose ring conforma=ons Pyranose ring conforma=ons Configura4onal and conforma4onal isomers Configura=onal: Enan=omers-‐ Stereoisomers that are mirror images; D-‐ or L-‐ based on configura=on at highest numbered chiral carbon. Configura=onal: Diastereomers-‐ Stereoisomers that are not mirror images; may have same D-‐ or L-‐ configura=on (or not). Configura=onal: Anomers-‐ Stereoisomers that differ in configura=on at the anomeric carbon (formerly the carbonyl C). Conforma=onal isomers-‐ Possess same stereochemical configura=on, but differ in three-‐ dimensional conforma=on. Monosaccharide derivatives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Phosphate esters Acids and lactones Alditols Amino sugars Glycosides Monosaccharide derivates- phosphate esters • Phosphate esters are important intermediates in the metabolism of sugars to provide energy – frequently formed by transfer of a phosphate group from ATP – fairly acidic (pKa1~ 1-2; pKa2~ 6-7) The hydrolysis of phosphate esters is thermodynamically favored For ATP: ΔG°’= -‐31 kJ/mol Monosaccharide derivatives- acids/lactones • Oxida=on of carbon to carboxyl – Glucose à gluconic acid – Oxida=on at C6à uronic acids – Aldonic and uronic acids can form stable lactones Monosaccharide derivatives- alditols • Reduc=on of the C=O group of a monosaccharide gives a polyhydroxy compound called an alditol Monosaccharide derivatives- amino sugars • Amino sugars have a hydroxyl of the parent monosaccharide replaced by an amino group Monosaccharide abbrevia=ons Monosaccharide derivatives- glycosides • Glycoside: a carbohydrate in which the -‐OH of the anomeric carbon is replaced by -‐OR • those derived from furanoses are furanosides; those derived from pyranoses are pyranosides • glycosidic bond: the bond from the anomeric carbon to the -‐OR group • This is the basis for the forma=on polysaccharides/ oligosaccharides Glycosidic bond formation Monosaccharide derivatives- glycosides • Cyclic monosaccharide + X-‐OH à O-‐glycoside • Cyclic monosaccharide + X-‐NH3à N-‐ glycoside Two different disaccharides of α-D-glucose • Glycosidic linkages can take various forms; the anomeric carbon of one sugar to any of the -OH groups of another sugar to forma an α- or β-glycosidic linkage Forma=on of maltose, a glucose-‐based disaccharide