* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Notes Part 1 for Ecology Test 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
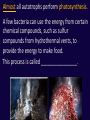
Principles of Ecology Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environment. Discuss with your table partner: Review the definitions of biotic and abiotic and identify examples of each. Biotic Factors: Abiotic Factors: Living organisms _________ parts of the environment. (and ___________). Examples: __________ __________ __________ Examples: __________ __________ __________ Levels of Organization: The Hierarchy of Life Organism: a living thing. Discuss with your table partner: Review the terms population, community and ecosystem. Explain the difference between these terms. Fill in your answers on the next 3 slides. Population: a group of organisms _____________ that live in the same area and can potentially interbreed. Community: A group of ___________that interact. Ecosystem: The interaction between populations in a community and the _________ ______________ (abiotic factors). Terrestrial Ecosystems: (Located on land) • Forests • Meadows • Desert Scrub Aquatic Ecosystems: • Ponds • Streams • Tide Pools Biome: A major region that shares similar _________ ___________and therefore similar plant communities. Population Density The number of organisms per unit of area. Population Density = _____________________ Examples of units: caterpillars/m2, fir trees/mi2 If there are 500 frogs in a rain forest that is 10 mi2, what is the population density of the frogs? A. 5000 frogs/ mi2 B. 5000 frogs- mi2 C. 50 frogs/ mi2 Correct Answer: ____________ D. 50 frogs-mi2 E. 5 frogs/mi2 F. 5 frogs-mi2 Roles in the Ecosystem Autotrophs: Organisms that can produce their ____ _____ using energy from the sun (or in a few cases certain chemical compounds). Another name for an autotroph is _____________. ___________________________________ Almost all autotrophs perform photosynthesis. A few bacteria can use the energy from certain chemical compounds, such as sulfur compounds from hydrothermal vents, to provide the energy to make food. This process is called ________________. Video: Bill Nye on Hydrothermal Vents (5.5 minutes) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D69hGvCsWgA Review with your table partner: Name similarities and differences between photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. Fill in similarities and difference on the next slide. Photosynthesis __________ __________ __________ __________ Chemosynthesis _________ _________ _________ ________ ____________ ____________ ____________ ____________ Heterotrophs: Organisms that get their energy from other organisms. Another name for a heterotroph is ______________. Types of Heterotrophs Herbivores: feeds only on ___________. Carnivores: feeds only on other animals. • Predators: kill other animals. • Scavengers: feed on ____________. Types of Heterotrophs Omnivores: Eat ______________ ____________________. Detritivores: Consume detritus (dead matter). Decomposers: Break down the complex molecules in dead plants and animals. Many bacteria and most fungi are decomposers. What would happen if there were no decomposers? __________________________ ___________________________ ______________. Discuss with your table partner: Identify an animal species that is a specialist and one that is a generalist. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each strategy? Fill in your answers on the next 2 slides. Specialist: species that feeds mainly (or completely) on _______ __________of food. Example: koalas feed on eucalyptus leaves. Advantage: Can usually ___________ other species for this food source. Specialists can have an advantage in a stable environment. Disadvantage: More vulnerable to environmental change, if ___________________. Generalist: species that feeds on a ____________ of food sources. Example: Raccoons Advantage: Has a broader niche. Usually better able to survive changes to the environment. Disadvantage: Generally ________________ ___________________for a food source.