* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force and Motion Study Guide 1. What is motion? What do we use to
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
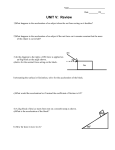
Force and Motion Study Guide Name: _________________________________ 1. What is motion? What do we use to help us determine if an object is in motion? Motion is the action or process of moving or of changing place or position. A place or object (reference point) is used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion. 2. Write the formula for speed. Calculate the speed of an object that has traveled 42 meters in 12 seconds. Speed = Distance/ Time S=42/12 S= 3.5m/s Name: _________________________________ Force and Motion Study Guide 18. Label Positive, Negative, and constant acceleration on the graph below. A. Positive B. Negative C. Constant 3. What is velocity? D. Positive Velocity is speed in a given direction. 4. What is a force? What unit do we use to measure force? Force is a push or pull. We measure force in Newtons (N). 5. How does each type of force affect the motion of an object? a. Balanced forces: Equal forces in each direction. There is no change to the motion (or acceleration) of the object. b. Unbalanced forces: Unequal forces acting on an object. There is change in motion (acceleration/deceleration). 6. When looking at a graph of motion, what does the slope of the line tell us? The slope tells us if the object is accelerating, moving at a constant speed or not moving at all. 7. What is acceleration? What unit do we use to measure acceleration? What are the three ways that acceleration can happen? Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes. The unit used to measure acceleration is meters/seconds/seconds or m/s2 Acceleration can happen when there is an increase in speed, decrease in speed or change in direction. 8. _______________ forces maintain motion at constant velocity. Balanced 9. _______________ forces acting on an object produce accelerated motion. Unbalanced 10. __________ is the tendency of an object to resist change in its motion. Inertia 11. To increase acceleration, one could decrease __________. mass/friction 12. A push or a pull, are both known as __________. forces 13. What is Net force? How we do draw an object with 50N of force pushing from the right and 20N of force pushing from the left? Net force is the overall force acting on an object. 20N 50N Use the graph to answer the following questions: 14. Name the two variables plotted in the graph. Distance and Time 15. Describe the object’s motion. Traveling at a constant speed 16. What is the distance traveled in three hours? 75 miles 17. What is the average speed the object traveled during the entire four hours? S=d/t 100/4 = 25mph 19. In what direction is the net force acting on the box? To the right 20. What does the head of the arrow indicate? The direction the force is moving the object 21. In what direction must a force be applied to balance the forces? To the left 22. If you apply a third force in a downward direction, how will the acceleration change? It will move down and to the right