* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Geometry MIDTERM REVIEW
Survey
Document related concepts
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
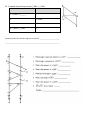
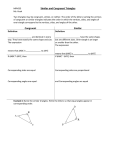
Honors Geometry MIDTERM REIVEW Transformations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Graph A(3, 2) B(2, 4) and C(1, 3) to form ΔABC. Find the midpoint of every side of ΔABC. How long is each side? Draw each midsegment and state their lengths. Translate ΔABC under the rule (x-4, y+2). Rotate ΔABC 90° clockwise. Reflect ΔABC over the x axis then the y-axis. Does ΔABC have any line or rotational symmetry? Equations of lines Line a can be described by the equation y 3 x 6. 5 9. Write an equation of a line that is parallel to line a? 10. Write an equation of a line that is perpendicular to line a? Parallel Lines Use the figure below to answer questions 11–14. Lines r and s are parallel. 11. State a pair of alternate interior angles? What is true about these angles? 12. State a pair of same-side interior angles? What is true about these angles? 13. Which of these explains why 4 8 ? A vertical angles theorem B alternate interior angles theorem C corresponding angles theorem 14. If m4 = (3y +1)°, m3 = 116° and m6 = (2x)°, write and solve equations to find x and y. Congruent Triangles 15. Draw an example of each of the triangle congruency theorems. SSS SAS AAS ASA HL Use the figures below for 18–20. Given 16. What is mB ? ABC PQR 17. What is PR? 18. By what theorem, postulate, or definition can you determine the angle and side measures for the figures above? _______________________________________________________________________________ Triangles 19. Can you make a triangle with sides 5cm, 6cm and 11cm? 20. In ΔMID, MI=15cm, ID=18cm and MD=22cm. State the angles from smallest to largest. For 21 & 22, use the figure. 21. If m1 53, what is m3? 22. Derrick states that DEF is an isosceles triangle. Is Derrick correct? Explain. Use ΔBCD for 23 & 24 23. Find the centroid for BCD. 24. What lines would you need in order to find the circumcenter? 25. Complete the proof to prove that ABC CDA. Statements Reasons 1. ACD ________ 1. 2. 2. Given 3. 3. 4. ABC CDA 4. Explain why side BC would be congruent to side AD. _________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ANSWERS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. ---(2.5,2) (1.5, 3.5) (2, 2.5) AB = √5, AC = √5 CB = √2 ---A’(-1, 4) B’(-2, 6) C’(-3, 5) (y, -x) A’’(2, -3) B’’(4, -2) C’’(3,-1) A’’’(-3, -2) B’’’(-2, -4) C’’’(-1, -3) One line of symmetry – no rotation y = 3/5x +/- and number y = -5/3x +/- and number Ex: 4 & 6 – congruent Ex: 5 & 4 – supplementary C y = 21; x = 32 ---92° 15 CPCTC No D, M, I 143° No, since two angles are not congruent, then two sides are not congruent. (-2, 2) Perpendicular Bisectors 25. Statements 1. ACD CAB 1. Given 2. BCA DAC 2. Given 3. AC CA 3. Reflexive Property of Congruence 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Reasons ABC CDA 4. ASA Triangle Congruence Theorem MPO PRQ 112° 44° Isosceles 19cm 120° True – By the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, RQS = RSQ so RS = RQ