* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Define HOLOCAUST
Survey
Document related concepts
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
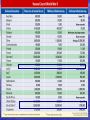
Whose on Whose side? Allies Axis (major powers) (major powers) Great Britain Germany Russia Italy United States Japan France (note: France surrendered to Germany in 1940 (after 6 weeks of fighting) Allies United: U.S.S.R, England and The U.S. European Front 1943 – German 6th Army surrenders at Stalingrad 1944 June 6 - D-Day: Allies land at Normandy Normandy Invasion, D-Day D-Day Landing on Normandy Beach European Front 1945 Feb. - FDR, Stalin, and Churchill meet at Yalta Conf. April 12 - FDR dies of a stroke April 28 - Mussolini Hanged by Italian Partisans April 30 - Hitler and wife commit suicide May 7 - Unconditional surrender of all German forces May 8 - V.E. Day (Victory in Europe) American generals: seated left to right are William H. Simpson, George S. Patton, Jr., Carl Spaatz, Dwight D. Eisenhower, Omar Bradley, Courtney H. Hodges, and Leonard T. Gerow; standing are Ralph F. Stearley, Hoyt S. Vandenberg, Walter Bedell Smith, Otto P. Weyland, and Richard E. Nugent. Define HOLOCAUST I. Holocaust 1. Great or total destruction, especially by fire. 2. a. Widespread destruction. b. A great disaster. 3. The genocide of European Jews and others by the Nazis during World War II 4. The deliberate and planned destruction of European Jews Pacific Front 1942 -April 10 – Bataan Death March -April 18 – Surprise U.S. “Doolittle” B-25 Raid on Tokyo -May 7-8 – Battle of the Coral Sea (first Japanese defeat) -June 4-5 – Battle of Midway – U.S. Victory (turning point of pacific front) 1944 - October 25 – The First Kamikaze attacks occur Pacific Front 1945 -May 20 – Japan withdraws from China -July 5 – Liberation of Philippines declared The Atomic Bomb I. The Bomb A. May 1942 •FDR sets up the Manhattan Project to prepare to build a bomb B. Truman was unaware of the Atomic Bomb at the time of FDR’s Death C. July 10th, 1945 •US test the Atomic Bomb - Los Alamos, NM D. July 26, 1945 • The Allies warn Japan E. August 6, 1945 • A B-29 ( the Enola Gay ) drops an atomic bomb on Hiroshima • 71,000 - 80,000 people die instantly F. August 9, 1945 • The US drops a Second bomb on Nagasaki G. Truman favors the dropping of the bombs because it would save American lives. – H. Japan Surrenders • • • • Japan announces their intent to surrender on August 12, 1945 August 14, 1945 Japan announces unconditional surrender August 15, 1945 - VJ Day Japan officially surrenders on September 2, 1945 aboard the US Battleship Missouri WW II Facts War Costs 1. US Debt 1940 - $9 billion US Debt 1945 - $98 billion The war cost $330 billion -- 10 times the cost of WWI & as much as all previous federal spending since 1776 24 B. Human Costs 25 WW II Facts Human Costs 50 million people died (compared to 15 million in WWI) 21.3 million Russians (7.7 million civilians) 11 million died as a result of the HOLOCAUST (6 million Jews + 5 million others) 26