* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MATH M16A: Applied Calculus Course Objectives (COR) • Evaluate
Survey
Document related concepts
Series (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
History of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Limit of a function wikipedia , lookup
Automatic differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Sobolev space wikipedia , lookup
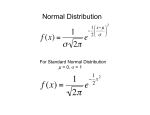
Distribution (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Lebesgue integration wikipedia , lookup
Multiple integral wikipedia , lookup
Lie derivative wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Neumann–Poincaré operator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
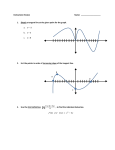
MATH M16A: Applied Calculus Course Objectives (COR) Evaluate the limit of a function, including one-sided and two-sided, using numerical and algebraic techniques and the properties of limits. Determine whether a function is continuous or discontinuous at a point. Calculate the derivative of an algebraic function using the formal definition of the derivative. Explain the concept of derivative as an "instantaneous rate of change" and the slope of the tangent line; find derivatives of functions using the constant, power, sum, difference, product, quotient, and chain rules, and using implicit differentiation. Find the derivative of algebraic, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Determine maxima and minima in optimization problems using the derivative. Sketch the graph of functions using the first and second derivatives to determine intervals where the functions are decreasing and increasing, maximum and minimum values, intervals of concavity and points of inflection. Solve applied problems involving tangent lines, rates of change and related rates. Apply the concept of derivative to solve applied problems involving marginal cost, profit and revenue, and growth and decay problems. Find definite and indefinite integrals by using general integral formulas, integration by substitution, and integration tables. Use integration techniques to find the area under a curve and the area between two curves. Use calculus to analyze revenue, cost, and profit. Use integration in business and economic applications Course Learning Outcomes (CLO) Students completing this course will be able to find a limit of a function graphically. Students completing this course will be able to compute the derivative of an algebraic function. Students completing this course will be able to find a (linear) Marginal Cost function and interpret it. Students completing this course will be able to find the area between two curves.