* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 171 Major Types of Psychoactive Drugs
Survey
Document related concepts
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
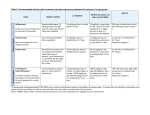
341770_ch_04.qxd 5/31/02 1:13 PM Page 171 mac76 mac76:568/sew: MODU LE 4.4 Concept 4.35 Drug abuse and dependence are complex problems arising from an interplay of social, biological, and psychological factors. 171 on the body (Leshner, 1999). Pressure from peers and exposure to family members who use alcohol or other drugs are important influences in leading young people to begin experimenting with drugs (“Peers Sway,” 2001; Simons-Morton et al., 2001). Some young people who feel alienated from mainstream culture come to identify with subcultures in which drug use is sanctioned or encouraged, such as the gang subculture. While initiation into drug use may be motivated by the desire to “fit in” or appear “cool” in the eyes of peers, people generally continue using drugs because of the pleasurable effects of the drugs themselves. With prolonged use of a drug, the body comes to depend on a steady supply of it, leading to physiological dependence. As people become chemically dependent, they CONCEPT CHART 4.4 Hallucinogens Stimulants Depressants Major Types of Psychoactive Drugs Drug Potential for Psychological/ Physiological Dependence Alcohol Major Psychological Effects Major Risks Yes/Yes Induces relaxation, mild euphoria, and intoxication; relieves anxiety; reduces mental alertness and inhibitions; impairs concentration, judgment, coordination, and balance With heavy use, can cause liver disorders and other physical problems; in overdose, can cause coma or death Barbiturates and tranquilizers Yes/Yes Reduces mental alertness; induces relaxation and calm; may produce pleasurable rush (barbiturates) High addictive potential; dangerous in overdose and when mixed with alcohol and other drugs Opioids Yes/Yes Induces relaxation and a euphoric rush; may temporarily blot out awareness of personal problems High addictive potential; in overdose, may cause sudden death Amphetamines Yes/Yes Boosts mental alertness; reduces need for sleep; induces pleasurable rush; causes loss of appetite In high doses, can induce psychotic symptoms and cardiovascular irregularities that may lead to coma or death Cocaine Yes/Yes Effects similar to those of amphetamines but shorter-lived High addictive potential; risk of sudden death from overdose; in high doses, can have psychotic effects; risk of nasal defects from “snorting” MDMA (“Ecstasy”) Yes/Yes Mild euphoria and hallucinogenic effects High doses can be lethal; may lead to depression or other psychological effects; may impair learning, attention, and memory Nicotine Yes/Yes Increases mental alertness; produces mild rush but paradoxically may have relaxing and calming effects Strong addictive potential; implicated in various cancers, cardiovascular disease, and other physical disorders Caffeine Yes/Yes Increases mental alertness and wakefulness In high doses, can cause jitteriness and sleeplessness; may increase risk of miscarriage during pregnancy LSD Yes/No Produces hallucinations and other sensory distortions Intense anxiety, panic, or psychotic reactions associated with “bad trips”; flashbacks Marijuana Yes/No Induces relaxation and mild euphoria; can produce hallucinations In high doses, can cause nausea, vomiting, disorientation, panic, and paranoia; possible health risks from regular use