* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Potential, Potential Difference Volts A voltage source
Survey
Document related concepts
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
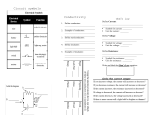
VOLTAGE CONCEPT QUESTIONS 1. What is another way to say voltage? Electric Potential, Potential Difference 2. What are the units of measure of voltage in the SI system? Volts 3. Why is voltage described as electrical potential? A voltage source provides a place of high potential energy and low potential energy for charges, like a water tower provides a place of high potential energy for water. 4. Is voltage a scalar or a vector? scalar 5. What is the electric potential in an outlet in your home? 120 Volts 6. What is the electric potential in a D-size battery? 1.5 volts 7. What is potential difference measured in? Volts 8. What is the circuit symbol for voltage? CURRENT CONCEPT QUESTIONS - CP 1. Define current. Flow of charge. 2. The current in a circuit is measured these units: Amperes (Amps) 3. Give the definition of one of these units: 1 Amp = 1 Coulomb/sec (C/s) 4. Current is measured with a(n) ammeter. The circuit symbol for this meter is: 5. What is the difference between alternating and direct current? Alternating current is current that moves back and forth and direct current moves in one direction. 6. What type of current is generated from a battery? (AC or DC?) 7. What type of current is provided in the outlet in your home? (AC or DC?) 8. Draw the direction of the current in the circuit below (note: proper circuit symbols not shown). 8. What is the purpose of a fuse or circuit breaker? To protect from high CURRENTS (not voltage…). RESISTANCE CONCEPT QUESTIONS 1. Define resistance: a measure of the difficulty of charge to flow 2. Resistance is measured in OHMS. 3. A wire with a resistance of 3 Ω has a (greater, lesser) resistance to electron flow than a wire with a resistance of 5 Ω. 4. The meter used to measure resistance is called an ohmmeter. 5. An ohm is defined as: the resistance through a circuit having a voltage of 1 volt and a current of 1 amp. 6. Name a group of elements that has a high resistance: non metals or insulators 7. Name a group of elements that have a low resistance: metals or conductors 8. Things that have a low resistance tend to be good (conductors, insulators). 9. Resistance (increases, decreases) as the length of a wire gets longer. 10. Resistance (increases, decreases) as the width of a wire gets wider. 11. Resistance (increases, decreases) as the temperature increases. 12. What is the circuit symbol for resistor? What is the symbol for a potentiometer?