* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download last year`s April exam
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
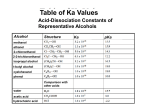
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
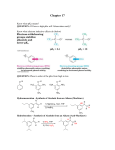
CHEMISTRY 150 April 2013 Dr. B. MacLean NAME: (please print) ___________________________________ ID #: ___________________________________ This is a three hour exam. Read over the entire exam before beginning, and begin by doing those questions which you find easiest. Ration your time according to the value of each question. There should be 16 pages in this exam (including this page). If your exam copy does not have 16 pages, notify me immediately. Answer all parts of this exam as indicated. For multiple choice questions, use the data card provided and hand this card in with your exam when you are finished. Be sure to indicate your name and ID number on this card and the exam. It is your responsibility to ensure that all of your answers are legible. READ ALL QUESTIONS CAREFULLY Questions Out of A1-30 30 B1 6 B2 4 B3 5 B4 12 B5 14 B6 5 B7 14 B8 10 TOTAL ____________ 100 1 Section A: Multiple choice - 30 points (1 each): Answer each of the following multiple choice questions on the computer card provided by shading the letter (a, b, c, or d) that corresponds to the best response in each case. 1) Which of the following compounds would not be considered to be an organic compound? a) ammonia b) methane c) aspirin (ASA) d) urea ((NH2)2CO) 2) The alpha particle emitted by some radioactive nuclei is identical to the nucleus of a ____________________ atom. a) hydrogen b) helium c) carbon d) deuterium 3) In terms of the kinds (or types) of organic reactions, alkenes and alkynes undergo mainly ____________________ type reactions, while aromatic compounds undergo mainly ____________________ type reactions. a) condensation; elimination b) elimination; substitution c) addition; condensation d) addition; substitution 4) Which of the following should possess the highest boiling point? a) 1,2-ethane diol b) ethanol c) 1,2,3-propane triol d) 2-pentanol 2 5) Which of the following types of compounds does not possess an acyl group? a) alcohol b) amide c) ketone d) ester 6) _______________ are commonly incorporated into perfumes and flavorings. a) thioethers b) mercaptans c) esters d) alkanes 7) For molecules that possess similar molecular weights, the proper ordering of boiling points (lowest highest) would be: a) alcohol, alkane, aldehyde, amine b) alkane, amine, aldehyde, alcohol c) amine, alkane, alcohol, aldehyde d) alkane, aldehyde, amine, alcohol 8) Which of the following compounds would be expected to be the most basic? a) ethanamide b) dimethylamine c) ethanoate ion d) ethanol 3 9) Which of the following compounds would represent a “free-base” structure? a) a) b) .HCl b) c) d) c) d) Cl- 10) What kind of constitutional isomerism is possible for alkanes? a) skeletal b) positional c) functional group d) cis-/trans- 11) The following reaction is known as a: a) saponification b) esterification c) amidification d) dehydration H2O K+ KOH 12) Which of the following acid/base combinations could be used to create a buffer mixture? a) HCl/NaCl b) HC2H3O2/NH3 c) HC2H3O3/NaOH d) NH3/NH4Cl 4 13) The reason that two alkenes having the same formula may be stereoisomers is that a) they possess a bond between the two double bond carbons b) -bonds do not allow for free-rotation between two atoms c) sigma bonds do not allow for free-rotation between two atoms d) double bonds consist of two bonds which do not permit twisting 14) One requirement for a carbon atom to be a chiral center is that it must be a) sp hybridized b) sp2 hybridized c) sp3 hybridized d) involved in a multiple bond 15) Which of the following molecules is chiral? a) 1-butanol b) 2-butanol c) benzene d) 1-bromopropane 16) From the following list of structures, which one is a hydrocarbon? a) butanone b) butyne c) butanoic acid d) 2-chloropropane 17) Which of the following compounds would be a carbohydrate? a) a) b) c) d) b) c) d) 5 18) The neurotransmitters Dopamine and Serotonin are examples of a) amines b) amides c) esters d) alcohols 19) Which of the following species would be a radical? a) OHb) OH c) H2O d) H3O+ 20) When some salt is dissolved into water, it is found that the pH of the solution is neutral. Which of the following salts might have been dissolved to create this solution? a) NaF b) NH4Cl c) NaBr d) KC2H3O2 21) Which of the following functional groups cannot form part of a ring in a heterocyclic compound? a) ester b) aldehyde c) amide d) ether 22) Which of the following structures represents an amino acid? a) a) b) b) c) d) c) d) 6 23) Which of the following compounds is capable of H-bonding to other molecules like itself? a) ethers b) alkanes c) ketones d) carboxylic acids 24) Which species shown would be expected to exhibit the greatest water-solubility? a) hexanoic acid b) sodium hexanoate c) hexane d) hexanol 25) Which of the following acid ionization constants corresponds to the weakest acid? a) Ka = 1.5 x 10-6 b) Ka = 1.0 x 10-6 c) Ka = 2.0 x 10-3 d) Ka = 1.5 x 10-2 26) Which of the following pKa values describes the strongest acid? a) pKa = 4.0 b) pKa = 10.0 c) pKa = 2.5 d) pKa = 1.0 7 27) The structure shown on the right is a a) primary amine b) secondary amine c) tertiary amine d) quaternary amine 28) The empirical formula for an alkyne would be a) CnH2n b) CnH2n-2 c) CnH2n-4 d) CnH2n+2 29) Combustion of an alcohol would be expected to yield a) CO2 and O2 b) CH4 and CO2 c) CO2 and H2O d) O2 and CH4 30) Two or more forms of an element which differ only in their numbers of neutrons are called a) isomers b) isotopes c) isochromic d) isostressedout 8 Section B: Long-answer problems - 70 points. Answer questions B1-B8. B1) Sodium hydroxide is used to titrate glutaric acid (IUPAC: pentane dioic acid), a dicarboxylic acid whose structure is shown below. During the titration, it was found that 25.0 mL of a glutaric acid solution required 15.9 mL of a 1.35 M sodium hydroxide solution to reach the endpoint. a) Write a balanced equation to describe the titration reaction [2] b) What is the concentration of the glutaric acid solution? [2] c) At the endpoint, would you expect the pH of the resulting solution to be acidic, basic, or neutral? [2] B2) A solution was made up by dissolving ammonia and ammonium chloride into water. The resulting solution had equal concentrations of NH3 and NH4+ ion. When a strong acid is added to this solution, the concentration of NH3 was found to drop to 0.50 M while the ammonium concentration became 0.65 M. Ka for ammonium ion is 5.55 x 10-10. a) What was the pH of this solution before the addition of the strong acid? [2] b) What was the pH of the solution after the addition of the strong acid? [2] 9 B3a) Selenium-75 (Z=34), a -emitter with a half-life of 120 days, is used medically for pancreas scans. Approximately how many grams of 75Se would remain from a 0.050 g sample that has been stored for a year? [2] b) What nuclide undergoes nuclear fission to produce barium-143, rubidium -94 and three neutrons? [1] c) List two requirements that must be met in order for a radionuclide to be used in a diagnostic treatment? [2] 10 B4) Draw the isomers indicated for each of the following: a) Draw a positional isomer of 3-methylcyclohexene [2] b) Draw a functional group isomer of butanone [2] c) Draw a skeletal isomer of 2,2-dimethylpropane [2] d) Draw the smallest alkane that has a chiral center. [2] e) The molecule shown below is called D-ribose, a sugar that is incorporated into the backbone of RNA in a cyclic form. Draw the enantiomer and a diastereomer of D-ribose. [4] D-ribose enantiomer diastereomer 11 B5) Of the following chemical reactions, complete a – d and three of the remaining four (e – h) reactions. Indicate the structure of the organic product(s) in each case. In cases where a major and minor product is possible (e.g. for certain addition reactions), only indicate the structure of the major product. [14] a) H2O HCl HCl b) c) H2O d) NaOH H2SO4 180oC (L.T.) Br2 e) f) g) h) FeBr3 (cat) [R] NaOH H+(cat) 12 B6a) List the following compounds in order of increasing boiling points: [3] N-methylpropanamide, butanamide, N,N-dimethylethanamide (lowest b.p.) _____________________ < _____________________ < _____________________ (highest b.p.) Answer b) or c) [2] b) Draw a picture that shows how water molecules can interact with an aldehyde through H-bonding, showing all possible interactions. c) Why are aldehydes having short carbon chains are able to dissolve in water, while longer-chain aldehydes are not water-soluble? 13 B7) Provide a name (IUPAC or common names are acceptable) for 7 of the following 8 organic structures shown below. [14] Cl- 14 B8) A laboratory experiment involving the chemical oxidation of three alcohols was carried out. These alcohols were labeled “A”, “B”, and “C”, but their actual identities were unknown. When the oxidation reaction was carried out on each of A, B, and C, it was found that C did not undergo oxidation, but A and B did (see below). The oxidized products, “D” and “E” were tested with Benedict’s solution. For E, Benedict’s test yielded a brick-red precipitate, while for D, the reagent remained unchanged. The possible identities of the alcohols (A – C) are given below. Using this information, draw structures for A - F in the fields indicated. [10] Possible starting alcohols: 2-butanol, 2-methyl-2-propanol, 2-methyl-1-propanol A [O] B C [O] D Benedict's solution E F Benedict's solution [O] 15 Formulas, constants moles _ of _ solute L _ of _ solution C1V1 C2V2 M pH log[ H 3O ] 10 pH [ H 3O ] pH pK a log pK a log K a [ A ] [ HA] [ H 3O ][OH ] K w 1x10 14 pH pOH 14.00 given _ units desired _ units desired _ units given _ units [C ] y [ D] z K eq [ A]w [ B ] x wA xB yC zD HA H 2O H 3O A incr. priority B H 2O BH OH IUPAC Priority carboxylic acid aldehyde ketone alcohol amine 1 amount _ remaining starting _ amount n 2 Have a great summer! 16











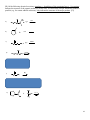












![Reduction [H]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007148356_1-25f5210a5c809c157bb6e0d32d66fd9d-150x150.png)
