* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the
Survey
Document related concepts
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Demersal fish wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
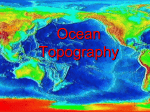
Study Notes for Chapter 19: The Ocean Basins Directions: Use the following notes to complete your study notes and then to prepare for the test. Please do not take this copy from the classroom. Thank you. Chapter 19 Section 1: The Water Planet 1. Earth’s oceans cover about ¾ th’s of Earth’s surface. 2. Of all the water on Earth, 97% is found in the oceans. 3. The deepest and largest ocean on Earth is the Pacific. 4. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a sea. 5. Drilling ships, sonar, and bathyscaphs are tools used by scientists to study the deep ocean. 6. A piece of sediment collected by drilling is a core sample. 7. Scientists use sonar to calculate the depth of the ocean floor. 8. SONAR stands for “SOund Navigation And Ranging”. 9. The first step in a sonar transmission is to send out a series of sound waves. 10. Sonar uses sound waves to measure the sea floor. 11. To see the bottom of the ocean for him or herself while remaining connected to a research ship, a scientist would use a bathysphere. Chapter 19 Section 2: Features of the Ocean Floor 12. Continental margins are made up of the continental rise, continental slope, and continental shelf. 13. A continental shelf is part of the continental margin. 14. The continental shelf has a gentle slope and usually has less than 100 meters of water above it. 15. Erosion from turbidity currents creates submarine canyons and the continental rise. 16. Sediments from rivers spread over the deep-ocean basins by means of turbidity currents. 17. The Mariana Trench is best known for its depth. 18. The deepest place in Earth’s crust is a trench. 19. Convergent plate boundaries cause deep ocean trenches. 20. The flattest regions on Earth are abyssal plains. 21. Ocean sediments are thinnest on the abyssal plains. 22. A nodule is made up of minerals. 23. Most mid-ocean ridges form below sea level. 24. The mid-ocean ridges in Iceland are unusual because they rise above sea level. 25. Seamounts are most likely to form in hot spots. In addition to these notes study the diagram on the top of pages 476-477 so that you can identify the different features found on the seafloor including the following: continental shelf, continental slope, continental rise, trench, mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plain, and seamount.