* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquake Unit Assessment Retake Preparation
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
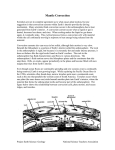
Name: ________________________________________________ Period: __________ Date: ____________________________= Earthquake Unit Assessment Retake Preparation Guide Key Unit Vocabulary Objective: Understand the meaning of key science vocabulary and be able to use correctly in a sentence. Core (Inner / Outer) Mantle Crust (Oceanic/Continental) Plate Tectonics Lithosphere Asthenosphere Continental Drift Pangaea Convergent Divergent Transform Subduction Sea-floor Spreading Trench Mountain (Volcanic / Uplift) Mid-Ocean Ridge Radiation Conduction Convection/Convection Current Density • Tip: Write the definition of each of science vocabulary word and draw a picture to illustrate meaning. Lesson 14: Earth’s Interior Objective: Be able to identify the interior layers of the Earth, along with the key characteristics of each. Reference materials: Earth’s Composition & Structure notes, Earth’s Interior notes, Lesson 14 Quiz, textbook pg. 167, ScienceSaurus section 177 1) Draw a diagram of the Earth’s four main interior layers: crust, mantle, outer core, inner core; then, write 2-3 characteristics of each layer. 2) Draw a diagram of the lithosphere and asthenosphere and explain the key characteristics of each. • Tip: Re-draw and label diagrams of Earth’s interior, make flashcards (name of layer/characteristics), review/correct your Lesson 14 Quiz, re-read textbook page 167 and ScienceSaurus section 177, etc. Lesson 15: Types of Boundaries: Objective: Be able to identify the 3 major types of plate boundaries, how each occurs, the direction of movement, and the landform(s) that result. Reference materials: Lab 15:1, Lab 15.2, Lab 15.3b, Notes on Plate Movement, Plate Movement Checkpoint, textbook pgs. 174-5 and 182-3 3) Draw diagrams of the three types of plate boundaries: convergent (C-C, O-C, O-O), divergent (O-O, transform (any combination); then, write the characteristics of each. 4) What type of plate boundary is the only one that creates new lithosphere (is constructive)? • Tip: Create note cards from your Notes on Plate Movement Note (boundary, plates involved, direction of movement, landform created, examples, etc.). Review and correct your Plate Movement Checkpoint grid. Lesson 16: Convection in the Mantle Objective: Understand how heat transfers in Earth’s interior and results in convection in the mantle as well as the movement of lithospheric plates. Reference Material: Convection in the Mantle (Lava Lamp Demo), Lesson 16 links (on website) 5) Write the definition for each type of heat transfer and draw a picture to illustrate meaning: Radiation Write a definition Draw a picture ----------------------------------------------------------------------Conduction Write a definition Draw a picture ----------------------------------------------------------------------Convection Write a definition Draw a picture ----------------------------------------------------------------------Convection Current Write a definition Draw a picture 6.) How does heat transfer in Earth’s interior (what is source and how moves between layers)? 7.) How does convection in the mantle connect to plate movement? 8) On the diagram, label the following: continental crust, oceanic crust, mantle, core, asthenosphere, lithosphere, convection cell, convergent boundary, divergent boundary, ocean ridge, ocean trench, volcanic mountains • Tip: Review each question and practice writing a response (minimum of one robust paragraph) using key vocabulary words in your answer.