* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An active chain of volcanoes at p boundaries is called the Ring of F
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
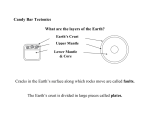
Plate Tectonics Review The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is believed to float on the “plastic” asthenosphere that is found just beneath it. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclusion that there are layers within the Earth. These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The outer core is the only true liquid layer. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthquakes, volcanic eruption, and the creation of mountains and ocean basins. Convection cells- within the mantle may the driving force for the movement of plates. Folded, tilted, faulted, and displaced rock layers suggest past crustal movement. The Earth is dynamic, constantly in motion. The surface shows evidence of past crustal movement. Continents fitting together like puzzle parts and fossil correlations provide initial evidence that continents were once connected. The large landmass was known as Pangaea. Continental Drift Theory Evidence: 1. Continents “fit!” 2. Fossils match up! 3. Rocks match up! 4. Landforms match up! The Theory of Plate Tectonics explains how the lithosphere consists of a series of plates that float on the partially molten section of the mantle (asthenosphere). Most volcanic activity and mountain building occur at the boundaries of these plates, often resulting in earthquakes. Plates may collide, move apart, or slide past one another. An active chain of vo boundaries is called Converging boundaries may have subduction taking place. The more dense crust (often oceanic) slides be crust that is less dense. Seafloor spreading results in the creation of new crust.