* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes - J Co Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
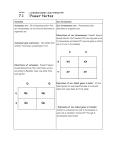
Sex Linked Traits | DAT Sex Chromosomes • Human chromosomes can be mapped out in a chart called a karyotype • Everybody’s first 22 chromosomes are structurally identical o They appear as two homologous X’s • However, the structure of the 23rd chromosome differs between males and females o It appears as two X’s in females, and an X and a Y in males • • • • • Human Karyotype For both males and females, chromosomes 1-22 appear as two homologous X’s. The 23rd chromosome appears as two X’s in females, and an X & Y in males. • Genes carried on the 23rd chromosome are said to be sexlinked o Often, sex-linked traits are carried on the Xchromosome and not the Y-chromosome Colorblindness • Colorblindness is a sex-linked trait that is carried exclusively on the X-chromosome • Furthermore, it is a recessive trait o That is, someone will only be colorblind if they carry the recessive allele and no dominant allele to mask it Suppose we have a female and a male, neither of whom is colorblind But let’s suppose the female is heterozygous for colorblindness o That is, one of her Xchromosomes will carry the recessive, colorblind allele, and the other will carry the dominant allele o We will denote this as XXC, where the C denotes the recessive colorblindness allele Since she has the dominant allele on one X-chromosome, the colorblindness allele is masked o Though she is not colorblind, she is said to be a carrier for the allele So, the two parent’s 23rd chromosomes will be denoted as XXC and XY for the female and male, respectively If we want to predict whether or not their offspring will be colorblind, we put the sex chromosomes into a Punnett square and solve it Punnett Square for Colorblindness Inserting the parents’ sex chromosomes (green) into the Punnett square, we solve as normal. 1 © 2017 J Co Review, Inc., Accessed by Guest on 06-17-2017 Sex Linked Traits | DAT • • • • Evidently, there are four possible outcomes for the offspring If the offspring is female (it receives two X chromosomes), it can receive: o Two healthy X chromosomes (red square) Making her noncolorblind o One healthy X chromosome and one Xchromosome with the colorblindness allele (blue square) Since the dominant allele prevails, she will not be colorblind If the offspring is male (it receives an X & Y chromosome), it can receive: o Healthy X and Y chromosomes (orange square) Making him noncolorblind o A healthy Y chromosome and an X-chromosome with the colorblindness allele (purple square) Since the Ychromosome doesn’t carry the gene, the dominant allele is absent and so this male only has the colorblindness allele • He will be colorblind So, a female child has a 0% chance of being colorblind and a male child has a 50% chance of being colorblind 2 © 2017 J Co Review, Inc., Accessed by Guest on 06-17-2017