* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Δx = vxt 32 m = 16 m/s
Survey
Document related concepts
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
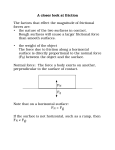
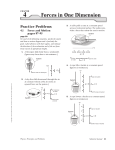
First you have to find the components of the initial velocity. vy = 20sin37o = 12 m/s 20 m/s 37o vy vx = 20cos37o = 16 m/s vx A) How long does it take to reach the fence? 32 m = 16 m/s (t) t = 2.0 s Δx = vxt B) How high (Δy) is it when it reaches the fence? 2 2 Δy = voyt + ½at = 12(2) + .5(-9.8)2 = 4.4 m The ball will be 1.9 m above the fence (4.4-2.5) C) On the axes below, sketch the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity of the ball as functions of time until the ball reaches the plane of the fence. The horizontal velocity is not affected by gravity and is constant. The vertical velocity is affected by -9.8 m/s2. It decreases approx. 10 m/s every second or 5 m/s every half second. 2A) FN = mg = (10 kg)9.8m/s2 = 100 N Ffr = μFN = .2(100 N) = 20 N Fnet = FA - Ffr = 50 N - 20 N = 30 N a = 3 m/s2 30 N = 10 kg(a) Fnet = ma 2B) Ffr FN T 10 kg FG T 5 kg FG 2C) The accelerating force is the same, but in this case the force accelerates a 10 kg and 5 kg block. a = 2 m/s2 30 N = 15 kg(a) Fnet = ma 3A) N1 and N2 have to provide a force equal to the weight of the person and the beam. N1 + N2 = (40kg + 50kg)9.8 m/s2 = 882 N B) N1 is no longer a force so the weight of the beam has to produce torque to balance the weight of the girl. N2 is the axis of rotation. 5m 40 kg Στc = Στcc 40kg(9.8 m/s2)5m = 50kg(9.8)d x = 4.0 m (from Δ) 50 kg Girl is 1.0 m from end X. d A 0.40 kg object moves in a straight line under the action of a net force. The graph above shows the velocity as a function of time for the object during a 25 s interval. At time t = 0, the object is at the position x = 0. Acceleration is the slope for each section. A) On the grid below, sketch a graph of the acceleration as a function of time for the object. Label the scale for the acceleration. B) Calculate the position of the object at t = 5.0 s. C) On which segment of the graph is the net force acting on the object zero? ____ A ____ B ____ C Justify your answer. D) Calculate the net force on the object during the first 3.0 s of the motion. E) Calculate the amount of work done on the object by the net force during the first 15 s of the motion. F) For the interval t = 15 s to t = 25 s, is the work done on the object by the net force positive, negative, or zero? ____ Positive ____ Negative ____ Zero Justify your answer.