* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights)
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
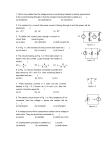
Check Your Understanding – Parallel Circuits – KEY (see highlights) 1. As more and more resistors are added in parallel to a circuit, the equivalent resistance of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases) and the total current of the circuit ____________ (increases, decreases). 2. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. Which one of the following statements is true? a. The current at Y is greater than the current at Q. Less than b. The current at Y is greater than the current at P. less than c. The current at Y is greater than the current at Z. equal d. The current at P is greater than the current at Q. e. The current at Q is greater than the current at P. less than f. The current is the same at all locations. false 3. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. At which location(s), if any, will the current be ... a. ... the same as at X? P b. ... the same as at Q? none c. ... the same as at Y? Z d. ... less than at Q? Y & Z e. ... less than at P? Q & Y & Z f. ... twice that at Z? Q g. ... three times that at Y? P & X 4. Which adjustments could be made to the circuit below that would decrease the current in the cell? List all that apply. a. Increase the resistance of bulb X. Yes b. Decrease the resistance of bulb X. No c. Increase the resistance of bulb Z. Yes d. Decrease the resistance of bulb Z. No e. Increase the voltage of the cell (somehow). No f. Decrease the voltage of the cell (somehow). Yes g. Remove bulb Y. Yes 5. A 12-V battery , a 12-ohm resistor and a 4-ohm resistor are connected as shown. The current in the 12-ohm resistor is ____ that in the 4-ohm resistor. a. 1/3 b. 1/2 c. 2/3 d. the same as e. 1.5 times f. twice g. three times h. four times 6. A 12-V battery , a 12-ohm resistor and a 4-ohm resistor are connected as shown. The voltage drop across the 12-ohm resistor is ____ that across the 4-ohm resistor. a. 1/3 b. 1/2 c. 2/3 d. the same as e. 1.5 times f. twice g. three times h. four times ANSWERS CAN BE FOUND AT: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/circuits/u9l4d.cfm