* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optical Microscopy and 4 Pi Microscopy
Fourier optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Fiber-optic communication wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
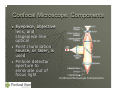
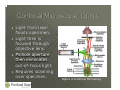
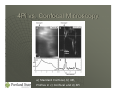
Optical Microscopy and 4 Pi Microscopy Carolyn A. Sutton PH 464 Overview The Optical Microscope • Resolution • Advantages and Disadvantages Confocal Microscopy 4 Pi Microscopy Optical Microscope for Metallography Optical Microscope: Origins Invented by either Hans and Zacharias Janssen or Galileo Galilei Galileo’s compound microscope Huygen’s two lens ocular system achromatically corrected A Modern Optical Microscope Optical Microscope: Components Eyepiece: used to focus and view subject Objective lens: used to enlarge subject Stagepiece: used to hold subject Illumination Source: used to light subject Parts of a Simple Optical Microscope Optical Microscope: Optics Objective lens close to subject creates enlarged inverted image inside tube. Compound eyepiece then focuses rays into virtual image for viewing Optics in Simple Compound Microscope Optical Microscope: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages: • Relatively easy to use • Samples analyzed in water or air • Samples shown in natural color • Magnifications are 100 – 1000X. Disadvantages: • Depth of focus decreases with increasing magnification • Resolving capability depends on wavelength of optical light (400 – 700 nm), objective lens, and sample itself. Confocal Microscope Improvement of optical microscope • Shallow depth of field • Elimination of outof-focus glare • Collection of optical sections from thick specimens Patented by Marvin Minsky in 1957 Confocal Microscope Confocal Microscope: Components Eyepiece, objective lens, and stagepiece like optical Point illumination source, or laser, is used Pinhole detector aperture to eliminate out of focus light Confocal Microscope Components Confocal Microscope: Optics Light from laser floods specimen. Light then is focused through objective lens. Pinhole aperture then eliminates out-of-focus light. Requires scanning over specimen. Optics in Confocal Microscopy Confocal Microscopy: Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages: • Improved 3D imaging. Disadvantages: • Does not really improve resolution of optical microscope (180 nm in focal plane and 500 nm along optic axis) Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Configuration 4Pi Microscopy Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STEM) provided resolution of up to 28 nm. Two microscope objectives with a common focus are used to increase microscope aperture. Aperture Angle in Microscopy 4Pi vs. Confocal Microscopy a) Standard Confocal, b) 4Pi, Profiles in c) Confocal and d) 4Pi Questions?