* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WELCOME TO PHYSICS 1103
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Solar cell efficiency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Rebound effect (conservation) wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
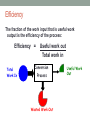
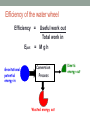
WELCOME TO 1103 PERIOD 8 Homework Exercise #7 is due today. Pick up the handout about Midterm 1 next Wednesday at 6:30 pm and the midterm review session next Tuesday at 6:30 pm PHYSICS 1103 – PERIOD 8 •How is energy conserved? •How can gravitational potential energy be used to do work with a water wheel? •What is the efficiency of multiple energy conversion processes? •Remember to put away your phone. No calls or texting during class. Law of conservation of energy • Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. • The total amount of energy we have now in the Universe is the same amount that existed at its beginning. • All the energy that goes into a conversion process must come out – no energy can be lost or destroyed. • In every energy conversion, some energy is wasted. • Wasted energy is often in the form of thermal energy from the force of friction. Kinetic energy The kinetic energy of a moving object is: E kin = ½Mv2 E kin = kinetic energy (joules) M = mass (kilograms) v = velocity (meters/sec) What happens to the kinetic energy of the two carts? Work Work is done when a force moves an object over some distance in the direction of the force. Work = Force x Distance W = FxD W = work (joules or foot-pounds) F = force applied (newtons or pounds) D = distance moved in the direction of the force (meters or feet) Work and energy are measured in units of joules. 1 joule = 1 kg m2/s2 Work done against friction Work is done to move the box horizontally against the force of friction. The work done goes into thermal energy. Applied Force Force of friction W=FxD Efficiency The fraction of the work input that is useful work output is the efficiency of the process: Efficiency = Total Work In Useful work out Total work in Conversion Process Wasted Work Out Useful Work Out Work done against gravity Work is done to raise an object vertically against the force of gravity. The work done goes into gravitational potential energy. Applied Force equals the weight of the box = Mg Force of gravity W=Mgh h = height the center of gravity of the object is raised Work to raise an object vertically The work required to lift an object equals the object’s weight times the vertical distance it moves. W = Mgh W = work (joules) M = mass of object (kilograms) g = acceleration of gravity = 9.8 m/s2 h = change in height (meters) Neglecting the energy wasted by friction, the gain in gravitational potential energy from raising an object equals the work done to raise it. Epot = M g h Efficiency of the water wheel Efficiency = Epot Gravitational potential energy in Useful work out Total work in = Mgh Conversion Process Wasted energy out Kinetic energy out Efficiency of multiple energy conversions Efficiency = Useful energy out Total energy in The overall efficiency of a series of energy conversions is the product of the efficiencies of each step. Overall Efficiency = Eff1 x Eff2 x Eff3 x ….. Example: 3 energy conversions steps with efficiencies of 40%, 50% and 20% have an overall efficiency of…. 0.40 x 0.50 x 0.20 = 0.04 = 4% America Revealed: Electric Nation 1) What energy processes are required to provide coal from the Powder River Basin in Wyoming to a power plant in Ohio? 2) A power plant burns coal to turn water into steam, which turns a turbine that generates electricity. What energy processes are required? 3) What is the main difference between a coal burning power plant and a nuclear plant? Which is more expensive to build? Why? 4) What energy processes are required to produce electricity from methane gas at the Blue Spruce dairy? 5) How does conservation of energy apply to each of the processes described above? BEFORE THE NEXT CLASS… Read textbook chapter 9 Complete Homework Exercise 8 Bring a blank Activity Sheet 9 to class. Study for midterm 1 Note: midterm 1 review session next Tuesday, 9/25, 6:30 – 7:30 pm in 2005 Smith Lab