* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Energy - Educator Pages
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
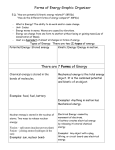
What is Energy? The ability to do work The ability to cause matter to move The ability to cause matter to change Measured in joules & calories Law of Conservation of Energy The amount of energy used to initiate a change is the same as the amount of energy detected at the end of a change. Chemical Energy Chemical Energy is the energy of a chemical compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy because it depends on the position and arrangement of the atoms in a compound. Example: food plants What is Potential Energy? Stored energy Energy of position The amount of usable energy in a body at rest, sometimes called Gravitational Potential Energy 2 Ways to Increase Potential Energy 1. Increase Height 2. Increase Mass Example: Stretching a rubberband Drawing back a bow and arrow Electrical Energy Electrical Energy is the energy of moving electrons. Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is used when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Example: Charging your iPod plugging in your flat iron What is Kinetic Energy? Energy of motion An object has kinetic energy due to it being in motion 2 ways to increase Kinetic Energy 1. Increase Mass 2. Increase Speed Example: A man running Riding a bicycle Mechanical Energy Example: listening to music talking to friends Thermal Energy Thermal Energy is all of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles that make up an object. All matter is made up of particles that are always in random motion. So, all matter has thermal energy. Thermal energy increases as temperature increases and increases as the number of particles increases potential energy + kinetic energy The mechanical energy of an object remains the same unless it transfers some energy to another object. Example: water in a waterfall Example: boiling water grilling a steak Light Energy Nuclear Energy Sound Energy Sound Energy is caused by an object’s vibrations. The object’s vibrations transmit some kinetic energy to the air particles, which also vibrate. These vibrations transmit sound energy. The total energy of motion and position of an object Can be found by adding Light Energy is produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles. Example: light bulb watching television Nuclear Energy is energy that comes from changes in the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear energy can be produced when nuclei are joined in a fusion reaction or when a nucleus is split apart in a fission reaction. Example: nuclear bomb nuclear power