* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problem Set
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
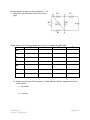
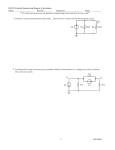
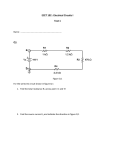
Name _______________________________________________________ Date ________________ AP PHYSICS 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set Suppose you have a 12-V voltage source, but you need only 4 V to power the electronic component in which you are interested. 1. Sketch a circuit that would allow you to get the desired voltage. Use standard conventions for illustrating the voltage source and resistor(s). Label the value of the voltage source and any resistors in your circuit. 2. Are there alternate solutions to the question above? If so, explain. If not, explain why not. 3. If an ammeters is not to significantly alter the circuit it is measuring, what must its resistance be? 4. If a voltmeter is not to significantly alter the circuit it is measuring, what must its resistance be? 5. Placing capacitors in series is typically a poor choice. Why? 6. Determine the equivalent resistance of the ‘ladder’ of equal 175 resistors, i.e., what would an ohmmeter read if it were connected to points A and B? Use the diagram at right to answer questions 7 – 14. 7. What is the net resistance of the circuit to the right? R1 R3 R5 R2 R4 R6 If each resistor is 5 and the voltage source is 10 V, complete the VIRP table. V I R P R1 Q9b Q9a 5 Q9c R2 Q10a Q10b 5 Q10c R3 Q11b Q11a 5 R4 Q12b Q12a 5 R5 5 R6 5 Total 10 Q8b Q8a Q8c 15. Suppose you have six 4.8 F capacitors. What will their effective capacitance be if you connect them… a. In parallel? b. In series? AP Physics 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set page 2 of 6 Suppose you place a constant voltage source between each of open terminals below. 16. In which circuit(s) (A-E) will current flow uninterrupted? Briefly explain. 17. In which circuit(s) will current flow then stop? Briefly explain. 18. In which circuits, if any, would current flow through the circuit after the voltage source were removed. 19. Suppose the resistor in circuit B were a light bulb. Sketch its brightness over time. (t=0 when the voltage is first applied to the circuit). Estimate the values of the resistors required to make intermittent windshield wipers: 20. One wipe every 15 seconds 21. One wipe every 4 seconds 22. One wipe every 2 seconds AP Physics 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set page 3 of 6 The circuit at the right has a total resistance of 15.0 k, and the battery supplies 24.0 V. If the time constant in the circuit below is measured to be 18.0 s, 23. calculate the total capacitance. 24. calculate how long it takes the resistor to reach 16.0 V after the switch is closed. AP Physics 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set page 4 of 6 In the lab, you connect a resistor and a capacitor with an unknown value in series with a battery that supplies a voltage of 12 V. When the switch is closed at time t = 0, the circuit is completed. Suppose you measure current through the circuit as a function of time. 𝑉 𝑡 When you plot your data, you find that 𝐼(𝑡) = 𝑅 𝑒 − ⁄4 25. Using common symbols for the battery, resistor, capacitor, and switch, draw the circuit that you constructed. Show the circuit before the switch is closed. Include whatever other devices you need to measure the current through the resistor to obtain the plot above. Label each component in your diagram. 26. Determine the value of the resistor in the circuit. 27. What was the capacitance of the capacitor? AP Physics 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set page 5 of 6 In the circuit shown to the right, the switch S is initially in the open position and the capacitor is initially uncharged. A graph of the capacitor’s voltage over time is shown at right. The battery has an emf of 20 V, the resistor R1 has a resistance of 15 k, and the capacitor has a capacitance of 20 F. 28. Determine the voltage across resistor R2 immediately after the switch is closed. 29. Determine the voltage across resistor R2 a long time after the switch is closed. 30. Calculate the value of the resistor R2. 31. On the graph below, sketch the current in R2 has a function of time from 0 – 15 s. Label the vertical axis with appropriate values. AP Physics 2 Circuits 3 Problem Set page 6 of 6