* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download maths - South Axholme Academy
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Birthday problem wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Laws of Form wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
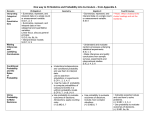
MATHEMATICS GRADE PROGRESSION SUMMARY Grade 9 Number Algebra Apply and interpret limits of accuracy To manipulate surds 9 Grade 8 Find the equation of a tangent to a curve at a given point Recognise and use the equation of a circle Plot and interpret graphs including reciprocals and exponentials Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change Interpret the gradient of a straight line graph as a rate of change Interpret the gradient at a point, on a curve, as the instantaneous rate of change Understand, construct and interpret equations that describe direct and inverse proportion Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Know and apply the sine and cosine rules to find unknown sides and angles Use vectors to construct geometric arguments and proofs Construct and interpret a histogram including unequal class intervals Calculate the probability for successive dependent events using tree diagrams and other representations All previous content is assumed and higher order thinking skills are required to solve problems interlinking topic areas Number Algebra Simplify surds such as 4(3 + √3) and (2-√3)(4 + √3) in the form a + b√3 Apply and interpret limits of accuracy Set up, solve and interpret the answers in growth and decay problems, including compound interest Derive harder algebraic proofs using reasoning and logic Understand trigonometric graphs for angles of any size Solve a pair of simultaneous graphs where one is linear and one is non-linear such as X+ 4y = 15 and x2 + y2 =9 Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change Compare lengths, areas and volume using ratio notation Interpret equations that describe direct and inverse proportion Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Use trigonometry to find sides and angles in 3-D Add, subtract and multiply vectors to solve geometry problems Transform the graphs of y=f(x) using transformations Interpret, analyse and compare the distributions of data sets through appropriate measures of median, mean, mode and range Calculate the probability for independent events using tree diagrams and other representations 8 Grade 7 Grade 6 Grade Ofqual states that to achieve grade 8, candidates will be able to: perform procedures accurately interpret and communicate complex information accurately make deductions and inferences and draw conclusions construct substantial chains of reasoning, including convincing arguments and formal proofs generate efficient strategies to solve complex mathematical and non-mathematical problems by translating them into a series of mathematical processes make and use connections, which may not be immediately obvious, between different parts of mathematics interpret results in the context of the given problem critically evaluate methods, arguments, results and the assumptions made Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion and Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Rates of Change Use index notation and Derive simple algebraic proofs Understand the Prove the circle theorems Use of mutually index laws for simple using reasoning difference between exclusive events Prove the construction fractional powers such as Recognise the shapes of direct and inverse and independent theorems 16¼ proportion events when solving functions Find bearings using probability problems Rationalise the Construct the graphs of loci, trigonometry denominator of a surd Interpret a including the circle x2 + y2 =r2 Calculate arc lengths, angles such as 2/√5 cumulative Use completing the square and areas of sectors of circles frequency diagram and the quadratic formula to Describe translations as 2-D solve quadratic equations vectors Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion and Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Rates of Change Convert recurring Simplify rational expressions Understand how to Use sine, cosine and tangent Use a cumulative decimals to fractions and involving quadratic use successive to calculate angles and sides frequency diagram vice versa expressions percentages written in a right angled triangle to estimate the as multipliers and to median and Work out reverse Complete tables for, and draw Bisect an angle and a straight be able to interpret interquartile range percentages graphs of reciprocal functions line the result Find the upper and lower Use reciprocal graphs to solve Combinations of bounds of simple equations transformations calculations (addition and Show step-by-step deductions subtractions) involving in providing a full quantities given to a mathematical explanation particular degree of Solve inequalities with accuracy unknowns on both sides Use index notation for multiplication and division Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion and Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics 5 Find the reciprocal of a number Find minimum and maximum values Divide a number by a decimal such as 1÷0.2 and 2.8 ÷0.07 Solving problems involving standard form Find a solution to a problem by forming an equation and solving it Draw graphs of harder quadratics such as y=x2 + 3x -5 Find the points of intersection of quadratic graphs with lines Use graphs to find the approximate solutions of quadratic equations Understand the difference between a demonstration (‘show me’) and a proof (‘prove…’) Show step-by-step deductions in providing a basic algebraic explanation Rates of Change Solve more difficult speed problems Calculate proportional changes using a multiplier Convert between measures of area and volume Construct angles and perpendicular lines Use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the height of an isosceles triangle Understand how to match one side and one angle of congruent triangles Use relative frequency to compare outcomes of experiments 5 Ofqual states that to achieve grade 5, candidates will be able to: perform routine single- and multi-step procedures effectively by recalling, applying and interpreting notation, terminology, facts, definitions and formulae interpret and communicate information effectively make deductions, inferences and draw conclusions construct chains of reasoning, including arguments generate strategies to solve mathematical and non-mathematical problems by translating them into mathematical processes, realising connections between different parts of mathematics interpret results in the context of the given problem evaluate methods and results Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion and Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Rates of Change Estimate answers to Solve problems involving Solve more complex Draw a quadrilateral such as a Calculate the mean calculations involving straight lines ratio and proportion kite of a parallelogram with for a frequency division problems, such as given measurements distribution Draw graphs of simple sharing out money Recall the cubes of 2, 3, quadratic functions such as Understand that the lengths of Find and compare between two groups 4, 5, and 10 y=x2 and y=x2+ 2 two sides and a non-included averages Grade 4 Grade 3 Grade 2 Perform calculations involving BIDMIS Do calculations with mixed numbers Number Algebra Round a number to one significant figure Calculate cubes and cube roots (with and without a calculator) Multiply whole and decimal numbers Divide numbers involving remainders Work out a percentage of an amount (with and without a calculator) Understand percentage, fraction and decimal equivalences Introduction to standard form Number Substitute negative numbers into a simple formula Complete a table of values for equations such as y=3x + 3 and draw the graph Read from a conversion graph for negative values Algebra Change a percentage to a fraction or a decimal and vice versa Arrange fractions in order of size Add and subtract negative integers in the ratio of their numbers Solve linear equations involving fractions Solve inequalities Plot points of a conversion graph and read off positive values Use a simple formula such as P=2w + 2h Solve simple equations such as x/2 =9 or 4x – 2 = 22 Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change Understand and interpret percentage changes Use reverse percentage to solve problems Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change Use ratio to solve simple problems involving recipes and ‘best buys’ angle do not define a unique triangle Find interior and exterior angles of an irregular polygon Perform reflections of shapes in diagonal lines Introduction to Pythagoras’ theorem Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Enlarge a shape by a positive scale factor Find the measurements of the dimensions of an enlarged shape Recognise congruent shapes Rotate and translate shapes Understand the idea of a locus Compare the mean and range of two distributions Understand mutually exclusive events Work with discrete and continuous data Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Understand the terms ‘perpendicular lines’ and ‘parallel lines’ Give the order of rotational symmetry of a 2-D shape Give a scale factor of an enlarged shape Compare two distributions using the range and one of the mode, median or mean Place probabilities on a number line Multiply and divide decimals to two places Round numbers to a given number of decimal places Recognise sequences involving square and cube numbers Plot the graphs of straight lines such as x=3 and y=4 Find the area and perimeter of compound shapes 2 Ofqual states that to achieve grade 2, candidates will be able to: Grade 1 recall and use notation, terminology, facts and definitions; perform routine procedures, including some multi-step procedures interpret and communicate basic information; make deductions and use reasoning to obtain results solve problems by translating simple mathematical and non-mathematical problems into mathematical processes provide basic evaluation of methods or results interpret results in the context of the given problem Number Algebra Find equivalent fractions Recognise cube numbers Add, subtract and multiply simple decimals Division of integers with no remainders Simplify fractions Multiply two digit numbers Simplify expressions Use a formula written in words, such as cost = 20 x distance travelled Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change Use ratio notationincluding writing it in its simplest form Geometry and Measures Probability and Statistics Use the word ‘congruent’ when triangles are identical Find the volume of a solid by counting cubes and stating units Recognise, name and sketch three- dimensional (3-D) solids Understand and use the vocabulary of probability Design and use tally tables for grouped data Find the median of an odd set of numbers Interpreting real life tables