* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
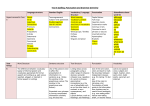
Year 5 Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation The information below gives guidance on the learning your child should be secure in by the end of the academic year. CONTENT WORD SKILLS Converting nouns or adjectives into verbs using suffixes Verb prefixes SENTENCE SKILLS Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that, or an omitted relative pronoun TEXT SKILLS PUNCTUATION SKILLS Indicating degrees of possibility using adverbs (for example, perhaps, surely) or modal verbs (for example, might, should, will, must) Devices to build cohesion within a paragraph Children may use then, after that, this, firstly, to effectively organise their writing for meaning. Linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials of time, place and number or tense choices cohesion Linking ideas using words/phrases that describe the action in a sentence using; Time, i.e. later Place, i.e. nearby Number, i.e. secondly Tense, i.e. he had seen her before An amplifying or explanatory word, phrase, or sentence inserted in a passage from which it is usually set off by punctuation including brackets, dashes and commas (see below) You can use commas to separate things in a list. You can also use them to mark out the less important part of a sentence (the dependent clause). The principal English modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will and would. Brackets are punctuation marks, used in pairs to set apart or interject text within other text. They are used to contain optional or additional material in a sentence that could be removed without destroying the meaning of the main text. Brackets may be used to add supplementary information, Relative clauses. Relative clauses are clauses starting with the relative pronouns who*, that, which, whose, where, when. They are most often used to define or identify the noun that precedes them. An amplifying or explanatory word, phrase, or sentence inserted in a passage from which it is usually set off by punctuation i.e. dash, bracket The dash (—) is a mark of punctuation used to set off a word or phrase after an independent clause or to set off a remark (i.e., words, phrases, or clauses that interrupt a sentence). To effectively organise their writing for meaning. ambiguity Something can be understood in more than one way. Brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis Use of commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity TERMINOLOGY modal verb These are the words your child should understand and be able to use correctly EXPLANATION Change names of objects and words that describe them in to action words by adding –ate; –ise; –ify Add prefixes to action words dis–, de–, mis–, over– and re– A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, whom, whose, which, that. The relative pronoun we use depends on what we are referring to and the type of relative clause. Adverbs are words that describe a verb. In this case perhaps, and surely may be used. Modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will and would. Certain other verbs are sometimes, but not always. bracket relative pronoun relative clause parenthesis dash